| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
where <math>h_n</math> is the length of an edge. Then the window function for this hypercube can be defined by | where <math>h_n</math> is the length of an edge. Then the window function for this hypercube can be defined by | ||
<div style="text-align: center;"> <math>\varphi(\textbf{u}) = \left\{ \begin{array}{ccc} 1, & |u_j| \leq \frac{1}{2} & j = 1, ..., d \\ 0, & else. & \end{array} \right.</math> </div> | <div style="text-align: center;"> <math>\varphi(\textbf{u}) = \left\{ \begin{array}{ccc} 1, & |u_j| \leq \frac{1}{2} & j = 1, ..., d \\ 0, & else. & \end{array} \right.</math> </div> | ||
| + | |||
<center> | <center> | ||
[[Image:pw_figure1a.png|800px]] | [[Image:pw_figure1a.png|800px]] | ||
| − | Figure 1. Given window function. (a) where <math>d</math> = 1, (b) where <math>d</math> = 2.</center> | + | Figure 1. Given window function. (a) where <math>d</math> = 1, (b) where <math>d</math> = 2. |
| − | + | </center> | |
| + | We simply shift this window function for <math>\textbf{x}_i</math> to determine if <math>\textbf{x}_i</math> belongs to the volume <math>V_n</math>, <math>\varphi(\frac{\textbf{x} - \textbf{x}_i}{h_n})</math>, and can compute the number of samples <math>k_n</math> falling in this volume using it: | ||
| + | <math><center> k_n = \displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^n \varphi(\frac{\textbf{x} - \textbf{x}_i}{h_n}).</math> </center> | ||
| + | In Parzen window method, therefore, the estimate for density <math>p_n(\textbf{x})</math> is | ||
| + | <math><center> p_n(\textbf{x}) = \frac{k_n/n}{V_n} = \frac{1}{n} \displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^n \frac{1}{V_n} \varphi(\frac{\textbf{x} - \textbf{x}_i}{h_n})</math>. </center> | ||
Revision as of 08:28, 30 April 2014
Parzen window method and classification
A slecture by ECE student Chiho Choi
Partly based on the ECE662 Spring 2014 lecture material of Prof. Mireille Boutin.
in progress....
Unlike parametric density estimation methods, non-parametric approaches locally estimate density function by a small number of neighboring samples [4] and therefore show less accurate estimation results. In spite of their accuracy, however, the performance of classifiers designed using these estimates is very satisfactory.
The basic idea for estimating unknown density function is based on the fact that the probability $ P $ that a vector x belongs to a region $ R $ [1]:
It can be rewritten as
if we assume a small local region $ R $, a large number of samples $ n $, and $ k $ of $ n $ falling in $ R $.\\ Suppose that the region $ R $ is a $ d $-dimensional hypercube around $ \textbf{x}_i \in \mathbb{R}^n $ in the rest of this slecture, and let the volume $ V_n $:
where $ h_n $ is the length of an edge. Then the window function for this hypercube can be defined by
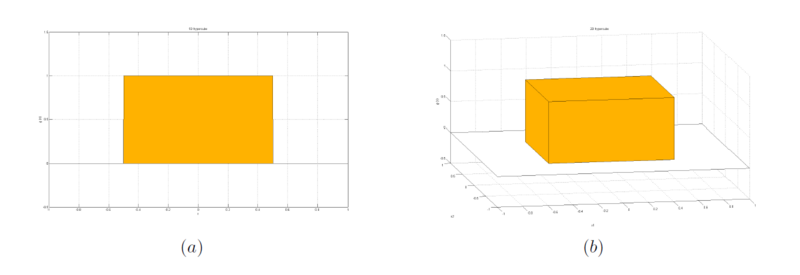 Figure 1. Given window function. (a) where $ d $ = 1, (b) where $ d $ = 2.
Figure 1. Given window function. (a) where $ d $ = 1, (b) where $ d $ = 2.
We simply shift this window function for $ \textbf{x}_i $ to determine if $ \textbf{x}_i $ belongs to the volume $ V_n $, $ \varphi(\frac{\textbf{x} - \textbf{x}_i}{h_n}) $, and can compute the number of samples $ k_n $ falling in this volume using it: $ <center> k_n = \displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^n \varphi(\frac{\textbf{x} - \textbf{x}_i}{h_n}). $ </center> In Parzen window method, therefore, the estimate for density $ p_n(\textbf{x}) $ is $ <center> p_n(\textbf{x}) = \frac{k_n/n}{V_n} = \frac{1}{n} \displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^n \frac{1}{V_n} \varphi(\frac{\textbf{x} - \textbf{x}_i}{h_n}) $. </center>
Post your slecture material here. Guidelines:
- If you are making a text slecture
- Type text using wikitext markup languages
- Type all equations using latex code between <math> </math> tags.
- You may include links to other Project Rhea pages.
$ \rightarrow $
Questions and comments
If you have any questions, comments, etc. please post them on this page.

