(New page: Category:ECE637 Category:sLecture Category:image processing Category:lecture notes sLecture :↳ [[ECE637_to...) |
|||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | = Excerpt from Prof. Bouman's Lecture = | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | =Accompanying Lecture Notes= | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Computed Tomography or CT is an imaging technique that uses an X-ray source and an array of detectors to produce tomographic images of an object. CT is commonly used in medical imaging for diagnosis. It also has applications in industry for imaging internal and external components. CT is also used in airport security. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In this set of notes, we will cover the basics of the physical design of CT scanners and derive the differential equation needed for the inversion process using convolution back projection. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Physical Design= | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:CT_fig1.jpeg|700px|thumb|left|A CT scanner]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
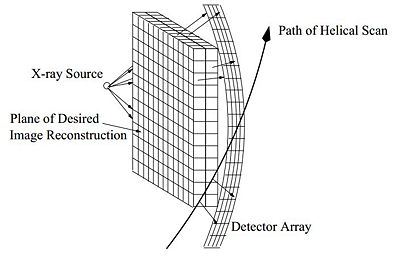
| + | Figure 1 shows a CT scanner for medical imaging. The patient lies down on the bed which is then translated through the scanner. The gantry is equipped with an X-ray source across from a detector array behind a fiberglass cover. The rays have a cone-beam structure. Figure 2 shows the orientation of the source and the detector array relative to the object being scanned. As the bed passes the rotating gantry, multiple data scans are collected and processed in real time. The path traced by the gantry relative to the patient is helical, hence the term helical multislice scan CT. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:CT_fig2.jpeg|400px|thumb|left|Multislice helical scan CT]] | ||
Revision as of 15:44, 6 May 2013
The Bouman Lectures on Image Processing
A sLecture by Maliha Hossain
Subtopic 2: Computed Tomography (CT)
© 2013
Excerpt from Prof. Bouman's Lecture
Accompanying Lecture Notes
Computed Tomography or CT is an imaging technique that uses an X-ray source and an array of detectors to produce tomographic images of an object. CT is commonly used in medical imaging for diagnosis. It also has applications in industry for imaging internal and external components. CT is also used in airport security.
In this set of notes, we will cover the basics of the physical design of CT scanners and derive the differential equation needed for the inversion process using convolution back projection.
Physical Design
Figure 1 shows a CT scanner for medical imaging. The patient lies down on the bed which is then translated through the scanner. The gantry is equipped with an X-ray source across from a detector array behind a fiberglass cover. The rays have a cone-beam structure. Figure 2 shows the orientation of the source and the detector array relative to the object being scanned. As the bed passes the rotating gantry, multiple data scans are collected and processed in real time. The path traced by the gantry relative to the patient is helical, hence the term helical multislice scan CT.