Contents
Practice Problem on Discrete-time Fourier transform computation
Compute the discrete-time Fourier transform of the following signal:
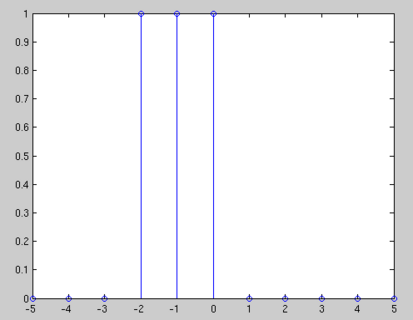
$ x[n]= u[n+2]-u[n-1] $
See these Signal Definitions if you do not know what is the step function "u[n]".
(Write enough intermediate steps to fully justify your answer.)
You will receive feedback from your instructor and TA directly on this page. Other students are welcome to comment/discuss/point out mistakes/ask questions too!
No need to write your name: we can find out who wrote what by checking the history of the page.
Answer 1
$ x[n] = u[n+2]-u[n-1] $.
$ X_(\omega) = \sum_{n=-\infty}^{+\infty} x[n] e^{-j\omega n} $
$ = \sum_{n=-2}^{0} x[n] e^{-j\omega n} $
$ = 1+ e^{j\omega} + e^{2j\omega} $
- Instructor's comment: Short and sweet. I like that.
Answer 2
$ X_{2\pi}(\omega) = \sum_{n=-\infty}^{+\infty} x[n] e^{-j\omega n} $
$ = \sum_{n=-2}^{0} x[n] e^{-j\omega n} $
$ = e^{2j\omega} + e^{j\omega} + 1 $
- Instructor's comment: It does help to visualize the signal first.
Answer 3
$ X(\omega) = \sum_{n=-\infty}^{+\infty} (u[n+2] -u[n-1]) e^{-j\omega n} $
$ = \sum_{n=-2}^{+\infty} u[n+2] e^{-j\omega n} - \sum_{n=1}^{+\infty} u[n-1] e^{-j\omega n} $
$ = \sum_{n=-2}^{0} (u[n+2] -u[n-1]) e^{-j\omega n} $
$ = e^{2j\omega} + e^{j\omega} + 1 $
Answer 4
$ x[n] = u[n+2]-u[n-1] $
$ x[n] = ((\delta[-2]) +(\delta[-1]) +(\delta[0])) $
so $ X[Z] = e^{2 j \omega} +e^{j \omega} +1 $
Answer 5
$ x[n] = u[n+2] - u[n-1] $
$ X_(\omega) = \sum_{n=-\infty}^{+\infty} x[n] e^{-j\omega n} $
$ X_(\omega) = \sum_{n=-2}^{0} e^{-j\omega n} $
$ X_(\omega) = 1 + e^{j\omega}+ e^{2j\omega} $
Answer 6
from the equation we can get that
$ X(n) = u[n+2] - u[n-1] = \left\{ \begin{array}{l l} 1 & \quad when \quad n = -2,-1,0\\ 0 & \quad \text{else} \end{array} \right. $
Hence, substitute into the DTFT equation,
$ X_(\omega) = \sum_{n = -\infty}^{ \infty} x[n] e^{-j\omega n} $
change the limit to
$ X_(\omega) = \sum_{n = -2}^{ 0} e^{-j\omega n} $
Then, we expand to the normal expression.
$ X_(\omega) = 1 + e^{j \omega} + e^{j 2 \omega} $
Answer 7
$ X(\omega) = \sum_{n=-\infty}^\infty x[n]e^{-j2\omega n} $
$ X(\omega) = e^{-j2\omega n}(\delta (n+2)-\delta (n+1)+\delta (n)) $ (Instructor's comment: The right-hand-side depends on n, but the left-hand-side does not. This means you made a mistake.)
$ X(\omega) = e^{-j2\omega} + e^{-j\omega} + 1 \ $
Answer 8
x[n] = u[n+2]-u[n-1]
$ X(\omega) = \sum_{n=-\infty}^\infty x[n]e^{-j\omega n} $
$ = \sum_{n=-2}^0 x[n]e^{-j\omega n} $
$ = e^{j\omega 2}+e^{j\omega}+1 \ $