| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:2015 Spring ECE 201 Peleato]][[Category:2015 Spring ECE 201 Peleato]][[Category:2015 Spring ECE 201 Peleato]][[Category:2015 Spring ECE 201 Peleato]][[Category:2015 Spring ECE 201 Peleato]] | [[Category:2015 Spring ECE 201 Peleato]][[Category:2015 Spring ECE 201 Peleato]][[Category:2015 Spring ECE 201 Peleato]][[Category:2015 Spring ECE 201 Peleato]][[Category:2015 Spring ECE 201 Peleato]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:ECE201]] | [[Category:ECE201]] | ||
| Line 25: | Line 21: | ||
==Question== | ==Question== | ||
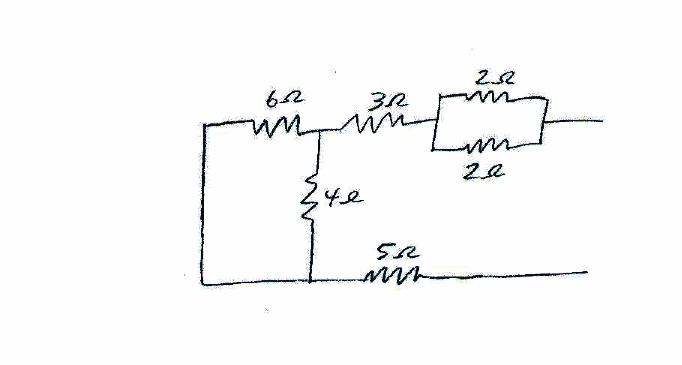
Determine the equivalent resistance of the resistor network shown below. | Determine the equivalent resistance of the resistor network shown below. | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | <center> |
| − | + | [[Image:Resistor_Network_Paul.gif|700px]] | |
| + | </center> | ||
---- | ---- | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 40: | Line 37: | ||
[[ECE201|Back to ECE201]] | [[ECE201|Back to ECE201]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 08:21, 13 April 2015
Practice question for ECE201: "Linear circuit analysis I"
By: ECE student Paul Wonnacott
Topic: Equivalent Resistor Network
Question
Determine the equivalent resistance of the resistor network shown below.
Answer
First, combine the two 2 ohm resistors that are in parallel to get a 1 ohm resistor. Sum this with the 3 ohm since they are in series to get 4 ohms. Then combine the 6 and the vertically oriented 4 ohm resistors in parallel to get a 2.4 ohm resistor. Add this with the 4 and 5 ohms that are in series to get an equivalent resistance of 11.4 ohms.
Questions and comments
If you have any questions, comments, etc. please post them below