| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[Category:2015 Spring ECE 201 Peleato]][[Category:2015 Spring ECE 201 Peleato]][[Category:2015 Spring ECE 201 Peleato]][[Category:2015 Spring ECE 201 Peleato]][[Category:2015 Spring ECE 201 Peleato]] | ||
| + | [[Category:ECE201]] | ||
| + | [[Category:ECE]] | ||
| + | [[Category:ECE201Spring2015Peleato]] | ||
| + | [[Category:circuits]] | ||
| + | [[Category:linear circuits]] | ||
| + | [[Category:problem solving]] | ||
| − | |||
| + | <center><font size= 4> | ||
| + | '''Practice question for [[ECE201]]: "Linear circuit analysis I" ''' | ||
| + | </font size> | ||
| − | + | By: [[ECE]] student Paul Wonnacott | |
| − | By: [[ECE]] student Paul Wonnacott | + | |
Topic: Current Division | Topic: Current Division | ||
| − | + | </center> | |
---- | ---- | ||
==Question== | ==Question== | ||
| Line 25: | Line 33: | ||
==Questions and comments== | ==Questions and comments== | ||
If you have any questions, comments, etc. please post them below | If you have any questions, comments, etc. please post them below | ||
| − | + | *Question | |
| + | **Answer | ||
| + | *Question | ||
---- | ---- | ||
[[2015 Spring ECE 201 Peleato|Back to 2015 Spring ECE 201 Peleato]] | [[2015 Spring ECE 201 Peleato|Back to 2015 Spring ECE 201 Peleato]] | ||
[[ECE201|Back to ECE201]] | [[ECE201|Back to ECE201]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 16:12, 29 April 2015
Practice question for ECE201: "Linear circuit analysis I"
By: ECE student Paul Wonnacott
Topic: Current Division
Question
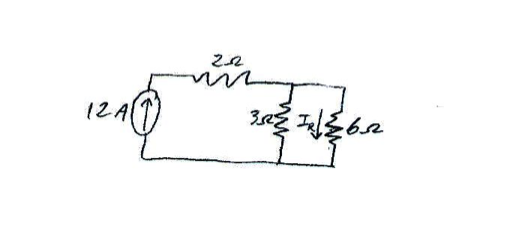
Determine the current IR in the figure below.
Answer
First, you can ignore the 2 ohm resistor since all the current needs to go through there. Then, apply the current division formula to the other two resistors. Take the 3 ohm resistor and divide by the sum of the 3 and 6 ohm resistors, and multiply this quantity by the 12 amps from the source. The answer is 4 amps.
Questions and comments
If you have any questions, comments, etc. please post them below
- Question
- Answer
- Question