(→Defining Distances Between Clusters) |
|||
| (25 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | = | + | =Lecture 24, [[ECE662]]: Decision Theory= |
| − | + | Lecture notes for [[ECE662:BoutinSpring08_Old_Kiwi|ECE662 Spring 2008]], Prof. [[user:mboutin|Boutin]]. | |
| − | + | Other lectures: [[Lecture 1 - Introduction_Old Kiwi|1]], | |
| + | [[Lecture 2 - Decision Hypersurfaces_Old Kiwi|2]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 3 - Bayes classification_Old Kiwi|3]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 4 - Bayes Classification_Old Kiwi|4]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 5 - Discriminant Functions_Old Kiwi|5]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 6 - Discriminant Functions_Old Kiwi|6]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 7 - MLE and BPE_Old Kiwi|7]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 8 - MLE, BPE and Linear Discriminant Functions_Old Kiwi|8]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 9 - Linear Discriminant Functions_Old Kiwi|9]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 10 - Batch Perceptron and Fisher Linear Discriminant_Old Kiwi|10]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 11 - Fischer's Linear Discriminant again_Old Kiwi|11]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 12 - Support Vector Machine and Quadratic Optimization Problem_Old Kiwi|12]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 13 - Kernel function for SVMs and ANNs introduction_Old Kiwi|13]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 14 - ANNs, Non-parametric Density Estimation (Parzen Window)_Old Kiwi|14]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 15 - Parzen Window Method_Old Kiwi|15]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 16 - Parzen Window Method and K-nearest Neighbor Density Estimate_Old Kiwi|16]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 17 - Nearest Neighbors Clarification Rule and Metrics_Old Kiwi|17]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 18 - Nearest Neighbors Clarification Rule and Metrics(Continued)_Old Kiwi|18]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 19 - Nearest Neighbor Error Rates_Old Kiwi|19]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 20 - Density Estimation using Series Expansion and Decision Trees_Old Kiwi|20]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 21 - Decision Trees(Continued)_Old Kiwi|21]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 22 - Decision Trees and Clustering_Old Kiwi|22]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 23 - Spanning Trees_Old Kiwi|23]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 24 - Clustering and Hierarchical Clustering_Old Kiwi|24]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 25 - Clustering Algorithms_Old Kiwi|25]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 26 - Statistical Clustering Methods_Old Kiwi|26]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 27 - Clustering by finding valleys of densities_Old Kiwi|27]], | ||
| + | [[Lecture 28 - Final lecture_Old Kiwi|28]], | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| − | + | == Minimum Spanning Tree Methods (MST) == | |
| + | One can find MST using [[Prim's Algorithm_Old Kiwi]] (fast test '57) or [[Krusal's Algorithm_Old Kiwi]] | ||
| − | + | === Kruskal's Algorithm === | |
| + | The algorithm starts with an initial empty tree, and it adds the edge with minimal cost to the tree at each step unless the edge creates a cycle. By repeating this process, it finds a Minimum Spanning tree. | ||
| − | + | [[Image:kruskal_Old Kiwi.gif|frame|center|Figure 1]] | |
| − | + | === Prim's's Algorithm === | |
| + | Prim's algorithm uses a connected tree as opposed to Kruskal's algorithm. Kruskal's Algorithm searches for minimum cost edge among all edges. Prim's Algorithm starts with the minimum cost edge, then it greedily searches for minimum cost edges among only adjacent edges. When every node is included in the tree algorithm stops. | ||
| − | 2 edges removed=> 3 clusters | + | [http://students.ceid.upatras.gr/~papagel/project/prim.htm Prim's Algorithm Demo ] |
| + | |||
| + | === Zahn's clustering algorithm (1971) === | ||
| + | *Find MST | ||
| + | *Identify "inconsistent" edges in MST and remove them. | ||
| + | |||
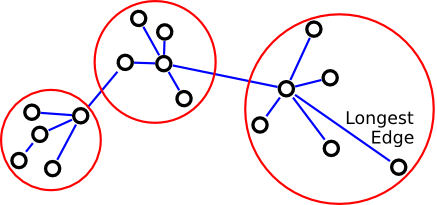
| + | e.g. remove the longest edge | ||
| + | #edge removed=> 2 clusters | ||
| + | #edges removed=> 3 clusters | ||
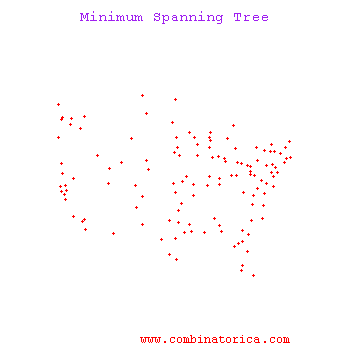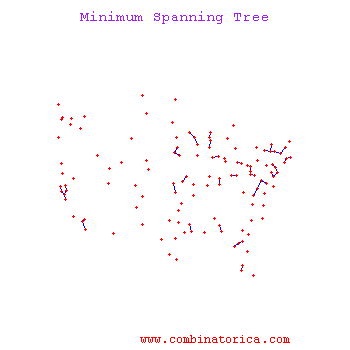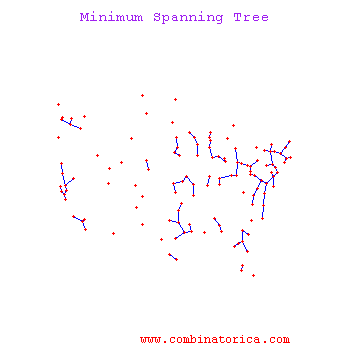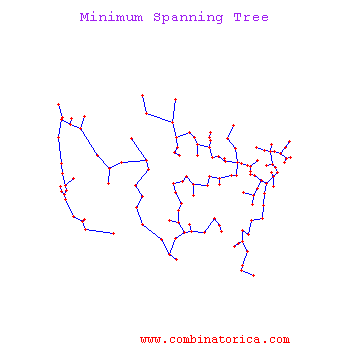
What if you have? | What if you have? | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Cluster_Old Kiwi.png|frame|center|Figure 2]] |
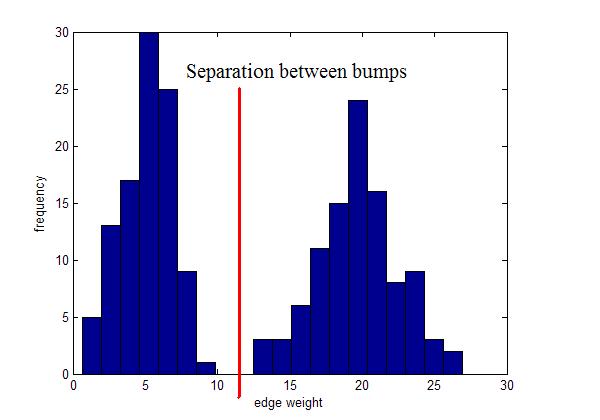
| − | Instead, use | + | Instead, use ''local'' inconsistency remove edges significantly larger than their neighborhood edges. |
Use for visualization | Use for visualization | ||
| − | [[Image:Lecture24Fig2_Old Kiwi.jpg]] | + | [[Image:Lecture24Fig2_Old Kiwi.jpg|frame|center|Figure 3]] |
== Visualizations of hierarchical clustering == | == Visualizations of hierarchical clustering == | ||
| + | [http://www.resample.com/xlminer/help/HClst/HClst_intro.htm Hierarchical Clustering]. | ||
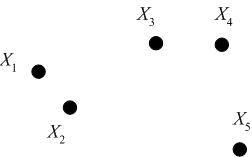
Consider the following set of five 2D data points, which we seek to cluster hierarchically. | Consider the following set of five 2D data points, which we seek to cluster hierarchically. | ||
| − | [[Image:Lecture23ClustersRaw_Old Kiwi.jpg]] | + | [[Image:Lecture23ClustersRaw_Old Kiwi.jpg|frame|center|Figure 4]] |
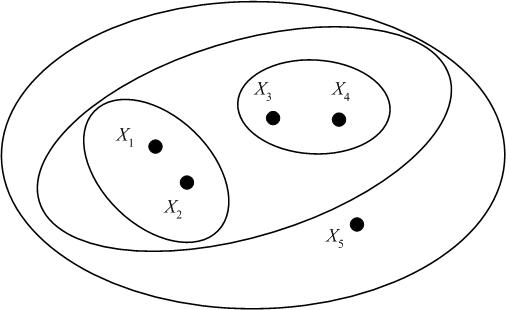
We may represent the hierarchical clustering in various ways. One is by a Venn diagram, in which we circle the data points which belong to a cluster, then subsequently circle any clusters that belong to a larger cluster in the hierarchy. | We may represent the hierarchical clustering in various ways. One is by a Venn diagram, in which we circle the data points which belong to a cluster, then subsequently circle any clusters that belong to a larger cluster in the hierarchy. | ||
| − | [[Image:Lecture23VennClusters_Old Kiwi.jpg]] | + | [[Image:Lecture23VennClusters_Old Kiwi.jpg|frame|center| Figure 5]] |
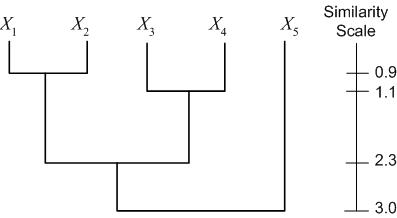
Another representation is a dendogram. A dendogram represents the clustering as a tree, with clusters that are more closely grouped indicated as siblings "earlier" in the tree. The dendogram also includes a "similarity scale," which indicates the distance between the data points (clusters) which were grouped to form a larger cluster. For the example dataset above (with distances calculated as Euclidian distance), we have the following dendogram: | Another representation is a dendogram. A dendogram represents the clustering as a tree, with clusters that are more closely grouped indicated as siblings "earlier" in the tree. The dendogram also includes a "similarity scale," which indicates the distance between the data points (clusters) which were grouped to form a larger cluster. For the example dataset above (with distances calculated as Euclidian distance), we have the following dendogram: | ||
| − | [[Image:Lecture23DendogramCluster_Old Kiwi.jpg]] | + | [[Image:Lecture23DendogramCluster_Old Kiwi.jpg|frame|center|Figure 6]] |
A third representation of hierarchical clustering is by using brackets. We bracket data points/clusters which are grouped into a cluster in a hierarchical fashion as follows: | A third representation of hierarchical clustering is by using brackets. We bracket data points/clusters which are grouped into a cluster in a hierarchical fashion as follows: | ||
<math>\{\{\{X_1,X_2\},\{X_3,X_4\}\},X_5\}</math> | <math>\{\{\{X_1,X_2\},\{X_3,X_4\}\},X_5\}</math> | ||
| − | |||
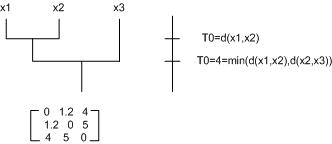
==Agglomerate Algorithms for Hierarchical Clustering (from Distances)== | ==Agglomerate Algorithms for Hierarchical Clustering (from Distances)== | ||
| Line 56: | Line 96: | ||
\end{pmatrix}</math>. For simplicity, assume that the distances are pairwise distinct, and sort distances in increasing order: <math>d_1, d_2, \cdots, d_{d/2}</math> | \end{pmatrix}</math>. For simplicity, assume that the distances are pairwise distinct, and sort distances in increasing order: <math>d_1, d_2, \cdots, d_{d/2}</math> | ||
| − | + | #Begin with clusters <math>S_1=\{X_1\}, S_2=\{X_2\}, \cdots, S_d=\{X_d\}</math> | |
| − | + | #Find the two nearest clusters <math>S_{i_0}, S_{j_0}</math> and merge them into a single cluster | |
| − | + | #Repeat step 2 until the number of clusters reaches a pre-specified number (the number 1 corresponds to a dendogram) | |
| − | + | ||
==Defining Distances Between Clusters== | ==Defining Distances Between Clusters== | ||
| − | Option 1 | + | ===Option 1=== |
| + | <math>{dist}(S_i, S_j) = \min_{X \epsilon S_i, X' \epsilon S_j}{dist}(X, X')</math> | ||
| − | We call this | + | We call this ''Nearest Neighbor Distance'' (NOT a distance, since <math>{dist}(S_i, S_j)=0 \not{=>} S_i=S_j</math>) |
This distance choice implies a "Nearest Neighbor (NN) clustering algorithm." Note: At each level of clustering, we have a "single-link clustering" with threshold <math>t_0=</math> distance between the last two clusters that were merged. | This distance choice implies a "Nearest Neighbor (NN) clustering algorithm." Note: At each level of clustering, we have a "single-link clustering" with threshold <math>t_0=</math> distance between the last two clusters that were merged. | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Park201_Old Kiwi.jpg]] | |
| + | '''Note''': If we continue until all <math>X_i</math>'s are linked, we get MST | ||
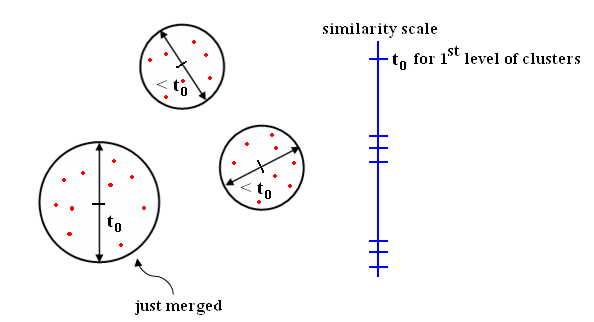
| − | Option 2 | + | ===Option 2=== |
| + | <math>{dist}(S_i, S_j) = \max_{X \epsilon S_i, X' \epsilon S_j}{dist}(X, X')</math> | ||
| − | We call this | + | We call this ''Farthest Neighbor (FN) Distance.'' |
| − | Effect: Increase cluster diameters as little as possible. | + | The Farthest Neighbor Algorithm is also known as The complete linkage clustering. The algorithm tries to estimate "How far the clusters are to each other". In order to find the distance between two clusters, It computes the distance between two farthest points (one from each cluster). |
| + | |||
| + | '''Effect''': Increase cluster diameters as little as possible. | ||
*At each level of clustering, you get a complete clustering. | *At each level of clustering, you get a complete clustering. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:LecFig_similarity_scale_Old Kiwi.PNG|frame|center|Figure 7 Farthest Neighbor distance with similarity scale]] | ||
| + | |||
Interpretation of NN and FN algorithm (Johnson-King 1967) | Interpretation of NN and FN algorithm (Johnson-King 1967) | ||
| Line 88: | Line 136: | ||
*If all objects belong to one single cluster, then stop. Else, goto (*). | *If all objects belong to one single cluster, then stop. Else, goto (*). | ||
| − | + | ===Generalization (Lance-William 1967)=== | |
| − | Generalization (Lance-William 1967) | + | |
Update similarity matrix using formula <math>{dist}(S_{i_0} \cup S_{j_0}, S_k) = \alpha_{i_0} d(S_{i_0},S_k)+\beta_{j_0} d(S_{j_0},S_k) + \gamma d(S_{i_0},S_{j_0}) + \delta |d(S_{i_0},S_k)-d(S_{j_0},S_k)|</math> | Update similarity matrix using formula <math>{dist}(S_{i_0} \cup S_{j_0}, S_k) = \alpha_{i_0} d(S_{i_0},S_k)+\beta_{j_0} d(S_{j_0},S_k) + \gamma d(S_{i_0},S_{j_0}) + \delta |d(S_{i_0},S_k)-d(S_{j_0},S_k)|</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Related Websites == | ||
| + | [http://www.people.vcu.edu/~gasmerom/MAT131/mst.html Minimum Spanning Algorithm] | ||
| + | * Definition | ||
| + | * Kruskal's algorithm | ||
| + | * Prim's algorithm | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.ececs.uc.edu/~cpurdy/lec21.html Minimu Spanning Trees] | ||
| + | * Greedy method | ||
| + | * Definition | ||
| + | * Kruskal's algorithm | ||
| + | * Prim's algorithm | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.cs.man.ac.uk/~graham/cs2022/greedy/ Greedy and Minimum Spanning Algorithms] | ||
| + | * Greedy algorithm | ||
| + | * Minimum spanning algorithm | ||
| + | * Kruskal's algorithm | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.studioreti.it/slide/05_MST_E_A.pdf Multiple Spanning Trees] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://ww3.algorithmdesign.net/handouts/MST.pdf Minmum Spanning Tress(Lecture Note)] | ||
| + | * Definition | ||
| + | * Prim-Jarnik's algorithm and example | ||
| + | * Kurskal's algorithm and example | ||
| + | * Baruvka's algorithm and example | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | [[ECE662:BoutinSpring08_Old_Kiwi|Back to ECE662, Spring 2008, Prof. Boutin]] | ||
Latest revision as of 08:43, 17 January 2013
Contents
Lecture 24, ECE662: Decision Theory
Lecture notes for ECE662 Spring 2008, Prof. Boutin.
Other lectures: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28,
Minimum Spanning Tree Methods (MST)
One can find MST using Prim's Algorithm_Old Kiwi (fast test '57) or Krusal's Algorithm_Old Kiwi
Kruskal's Algorithm
The algorithm starts with an initial empty tree, and it adds the edge with minimal cost to the tree at each step unless the edge creates a cycle. By repeating this process, it finds a Minimum Spanning tree.
Prim's's Algorithm
Prim's algorithm uses a connected tree as opposed to Kruskal's algorithm. Kruskal's Algorithm searches for minimum cost edge among all edges. Prim's Algorithm starts with the minimum cost edge, then it greedily searches for minimum cost edges among only adjacent edges. When every node is included in the tree algorithm stops.
Zahn's clustering algorithm (1971)
- Find MST
- Identify "inconsistent" edges in MST and remove them.
e.g. remove the longest edge
- edge removed=> 2 clusters
- edges removed=> 3 clusters
What if you have?
Instead, use local inconsistency remove edges significantly larger than their neighborhood edges.
Use for visualization
Visualizations of hierarchical clustering
Consider the following set of five 2D data points, which we seek to cluster hierarchically.
We may represent the hierarchical clustering in various ways. One is by a Venn diagram, in which we circle the data points which belong to a cluster, then subsequently circle any clusters that belong to a larger cluster in the hierarchy.
Another representation is a dendogram. A dendogram represents the clustering as a tree, with clusters that are more closely grouped indicated as siblings "earlier" in the tree. The dendogram also includes a "similarity scale," which indicates the distance between the data points (clusters) which were grouped to form a larger cluster. For the example dataset above (with distances calculated as Euclidian distance), we have the following dendogram:
A third representation of hierarchical clustering is by using brackets. We bracket data points/clusters which are grouped into a cluster in a hierarchical fashion as follows: $ \{\{\{X_1,X_2\},\{X_3,X_4\}\},X_5\} $
Agglomerate Algorithms for Hierarchical Clustering (from Distances)
Reference - Chapter 3.2 from Jain and Dudes ??
Begin with a matrix of pairwise distances:
$ \mathcal{D} = \begin{pmatrix} 0 & d_{1,2} & \cdots & d_{1,d} \\ d_{1,2} & 0 & \ddots & \vdots \\ \vdots & \ddots & \ddots & d_{d-1,d} \\ d_{1,d} & \cdots & d_{d-1,d} & 0 \end{pmatrix} $. For simplicity, assume that the distances are pairwise distinct, and sort distances in increasing order: $ d_1, d_2, \cdots, d_{d/2} $
- Begin with clusters $ S_1=\{X_1\}, S_2=\{X_2\}, \cdots, S_d=\{X_d\} $
- Find the two nearest clusters $ S_{i_0}, S_{j_0} $ and merge them into a single cluster
- Repeat step 2 until the number of clusters reaches a pre-specified number (the number 1 corresponds to a dendogram)
Defining Distances Between Clusters
Option 1
$ {dist}(S_i, S_j) = \min_{X \epsilon S_i, X' \epsilon S_j}{dist}(X, X') $
We call this Nearest Neighbor Distance (NOT a distance, since $ {dist}(S_i, S_j)=0 \not{=>} S_i=S_j $)
This distance choice implies a "Nearest Neighbor (NN) clustering algorithm." Note: At each level of clustering, we have a "single-link clustering" with threshold $ t_0= $ distance between the last two clusters that were merged.
Note: If we continue until all $ X_i $'s are linked, we get MST
Option 2
$ {dist}(S_i, S_j) = \max_{X \epsilon S_i, X' \epsilon S_j}{dist}(X, X') $
We call this Farthest Neighbor (FN) Distance.
The Farthest Neighbor Algorithm is also known as The complete linkage clustering. The algorithm tries to estimate "How far the clusters are to each other". In order to find the distance between two clusters, It computes the distance between two farthest points (one from each cluster).
Effect: Increase cluster diameters as little as possible.
- At each level of clustering, you get a complete clustering.
Interpretation of NN and FN algorithm (Johnson-King 1967)
- Input proximity matrix $ \mathcal{D}=(d_{i,j}) $
- Decide which cluster distance you will use (NN, FN, ...)
- Set scale = 0
- Begin with $ S_1=\{X_1\},S_2=\{X_2\},\cdots,S_d=\{X_d\} $
- (*) Find $ (S_{i_0},S_{j_0})=\underset{i \not{=} j}{argmin}({dist}(S_i,S_j)) $ from $ \mathcal{D} $
- Merge $ S_{i_0} $ & $ S_{j_0} $
- Update $ \mathcal{D} $ by deleting rows and columns $ i_0 $ and $ j_0 $; add a row and column for $ S_{d+1}=S_{i_0} \cup S_{j_0} $. Fill in new row and column with the chosen cluster distribution.
- If all objects belong to one single cluster, then stop. Else, goto (*).
Generalization (Lance-William 1967)
Update similarity matrix using formula $ {dist}(S_{i_0} \cup S_{j_0}, S_k) = \alpha_{i_0} d(S_{i_0},S_k)+\beta_{j_0} d(S_{j_0},S_k) + \gamma d(S_{i_0},S_{j_0}) + \delta |d(S_{i_0},S_k)-d(S_{j_0},S_k)| $
Related Websites
- Definition
- Kruskal's algorithm
- Prim's algorithm
- Greedy method
- Definition
- Kruskal's algorithm
- Prim's algorithm
Greedy and Minimum Spanning Algorithms
- Greedy algorithm
- Minimum spanning algorithm
- Kruskal's algorithm
Minmum Spanning Tress(Lecture Note)
- Definition
- Prim-Jarnik's algorithm and example
- Kurskal's algorithm and example
- Baruvka's algorithm and example