(New page: Category:ECE301Spring2011Boutin Category:problem solving = Practice Question on Computing the Fourier Series discrete-time signal= Obtain the Fourier series the DT signal <math> x...) |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:ECE301Spring2011Boutin]] | [[Category:ECE301Spring2011Boutin]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:ECE301]] |
| − | = Practice Question on Computing the Fourier Series | + | [[Category:signals and systems]] |
| − | Obtain the Fourier series the | + | [[Category:Problem_solving]] |
| + | [[Category:Fourier series]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | = [[:Category:Problem_solving|Practice Question]] on Computing the Fourier Series continuous-time signal= | ||
| + | Obtain the Fourier series the CT signal | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| − | x | + | x(t) = \left\{ |
\begin{array}{ll} | \begin{array}{ll} | ||
| − | 1, & \text{ for } -5\leq | + | 1, & \text{ for } -5\leq t \leq 5,\\ |
| − | 0, & \text{ | + | 0, & \text{ for } 5< |t| \leq 10, |
\end{array} | \end{array} | ||
\right. \ </math> | \right. \ </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | x(t) periodic with period 20. | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 17: | Line 23: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
===Answer 1=== | ===Answer 1=== | ||
| − | + | <math>k=0\,</math> | |
| + | |||
| + | <math>a_0=\frac{1}{20}\int_{-10}^{10}x(t)e^{-0}dt=\frac{1}{20}\int_{-5}^{5}1dt=\frac{1}{2}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>k\ne0</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>a_k=\frac{1}{20}\int_{-10}^{10}x(t)e^{-jkw_0t}dt=\frac{1}{20}\int_{-5}^{5}e^{-jk\frac{\pi}{10}t}dt=\frac{1}{20}\Bigg[\frac{e^{-jk\frac{\pi}{2}}-e^{jk\frac{\pi}{2}}}{-jk\frac{\pi}{10}}\Bigg]=\frac{1}{-jk2\pi}\Bigg(e^{-jk\frac{\pi}{2}}-e^{jk\frac{\pi}{2}}\Bigg)</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>x(t)=\frac{1}{2}e^{-jk\frac{\pi}{10}t}+\sum_{k=-\infty}^-1\frac{1}{-jk2\pi}\Bigg(e^{-jk\frac{\pi}{2}}-e^{jk\frac{\pi}{2}}\Bigg)e^{-jk\frac{\pi}{10}t}+\sum_{k=1}^\infty\frac{1}{-jk2\pi}\Bigg(e^{-jk\frac{\pi}{2}}-e^{jk\frac{\pi}{2}}\Bigg)e^{-jk\frac{\pi}{10}t}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | --[[User:Cmcmican|Cmcmican]] 21:35, 7 February 2011 (UTC) | ||
| + | |||
| + | :TA's comment: That looks fine. The expression for <math>a_k</math> is better written in terms of a sin function, though. Regarding the synthesis of <math>x(t)</math>, you got it wrong actually. The complex exponentials should not have a minus sign in their exponents and for <math>k=0</math> the complex exponential has a frequency of zero (DC). | ||
| + | |||
| + | :Another thing is that you may also further simplify <math>x(t)</math> and write it in terms of sin waves only. You will actually notice some pattern in the frequencies of these sin waves. | ||
===Answer 2=== | ===Answer 2=== | ||
| − | + | First I plotted it out, thanks to WolframAlpha [[Image:EthanHall_ECE301_S11_Wolframalpha-20110215211454118.gif]] | |
| + | |||
| + | Then I used the equation <math class="inline"> a_{k} = \frac{1}{T}\int_{0}^{20}x(t)e^{-jk(\frac{2\pi}{T})t}dt </math> where T = 20. You can change the limits of the integral to -10 and 10 since the function is periodic. We just need it over one period. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Solving for <math class="inline">a_{0}</math> first we get <math class="inline"> a_{0} = \frac{1}{20} \int_{-10}^{10}x(t)e^{-j(0)(\frac{2\pi}{20})t}dt </math>. We know that x(t) = 0 except for -5 < t < 5 where it is 1. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> a_{0} = \frac{1}{20} \int_{-5}^{5}(1)e^{(0)}dt = \frac{1}{20}x \bigg|_{-5}^{5} = \frac{1}{2} </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math > a_{k} = \frac{1}{20}\int_{-5}^{5}(1)e^{-jk(\frac{2\pi}{20})t}dt; \text{ where } -5 < k <5 \text{ and }k \neq 0 </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math > a_{k} = \frac{1}{20} \left[ \frac{e^{-jk(\frac{\pi}{10})t}}{-jk(\frac{\pi}{10})}\right]_{-5}^{5} </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math >a_{k} = \frac{1}{20}\left(\frac{1}{-jk\frac{\pi}{10}}\right) \left[ e^{-jk(\frac{\pi}{10})5} - e^{-jk(\frac{\pi}{10})(-5)} \right] </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>a_{k}= \frac{-1}{2jk}\left[ e^{-\frac{jk\pi}{2}} - e^{\frac{jk\pi}{2}} \right]\text{ for }-5 < k < 5\text{ and }k \neq 0\text{, all others }0</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>x(t) = \sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty}a_{k}e^{jk\frac{2\pi}{T}t}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>x(t) = \sum_{k=-5}^{-5} a_{k}e^{jk\frac{ \pi}{10}t}</math> I changed the limits of the sum because <math class="inline">a_{k}</math> is 0 for anything outside that range. | ||
| + | |||
===Answer 3=== | ===Answer 3=== | ||
Write it here. | Write it here. | ||
---- | ---- | ||
[[2011_Spring_ECE_301_Boutin|Back to ECE301 Spring 2011 Prof. Boutin]] | [[2011_Spring_ECE_301_Boutin|Back to ECE301 Spring 2011 Prof. Boutin]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:59, 16 September 2013
Contents
Practice Question on Computing the Fourier Series continuous-time signal
Obtain the Fourier series the CT signal
$ x(t) = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} 1, & \text{ for } -5\leq t \leq 5,\\ 0, & \text{ for } 5< |t| \leq 10, \end{array} \right. \ $
x(t) periodic with period 20.
You will receive feedback from your instructor and TA directly on this page. Other students are welcome to comment/discuss/point out mistakes/ask questions too!
Answer 1
$ k=0\, $
$ a_0=\frac{1}{20}\int_{-10}^{10}x(t)e^{-0}dt=\frac{1}{20}\int_{-5}^{5}1dt=\frac{1}{2} $
$ k\ne0 $
$ a_k=\frac{1}{20}\int_{-10}^{10}x(t)e^{-jkw_0t}dt=\frac{1}{20}\int_{-5}^{5}e^{-jk\frac{\pi}{10}t}dt=\frac{1}{20}\Bigg[\frac{e^{-jk\frac{\pi}{2}}-e^{jk\frac{\pi}{2}}}{-jk\frac{\pi}{10}}\Bigg]=\frac{1}{-jk2\pi}\Bigg(e^{-jk\frac{\pi}{2}}-e^{jk\frac{\pi}{2}}\Bigg) $
$ x(t)=\frac{1}{2}e^{-jk\frac{\pi}{10}t}+\sum_{k=-\infty}^-1\frac{1}{-jk2\pi}\Bigg(e^{-jk\frac{\pi}{2}}-e^{jk\frac{\pi}{2}}\Bigg)e^{-jk\frac{\pi}{10}t}+\sum_{k=1}^\infty\frac{1}{-jk2\pi}\Bigg(e^{-jk\frac{\pi}{2}}-e^{jk\frac{\pi}{2}}\Bigg)e^{-jk\frac{\pi}{10}t} $
--Cmcmican 21:35, 7 February 2011 (UTC)
- TA's comment: That looks fine. The expression for $ a_k $ is better written in terms of a sin function, though. Regarding the synthesis of $ x(t) $, you got it wrong actually. The complex exponentials should not have a minus sign in their exponents and for $ k=0 $ the complex exponential has a frequency of zero (DC).
- Another thing is that you may also further simplify $ x(t) $ and write it in terms of sin waves only. You will actually notice some pattern in the frequencies of these sin waves.
Answer 2
First I plotted it out, thanks to WolframAlpha 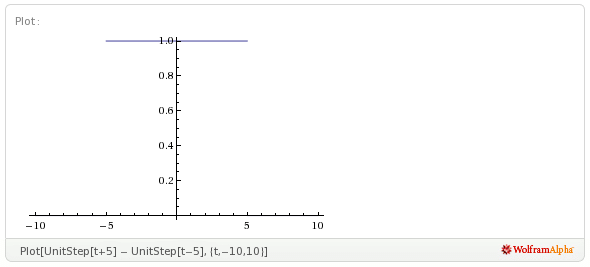
Then I used the equation $ a_{k} = \frac{1}{T}\int_{0}^{20}x(t)e^{-jk(\frac{2\pi}{T})t}dt $ where T = 20. You can change the limits of the integral to -10 and 10 since the function is periodic. We just need it over one period.
Solving for $ a_{0} $ first we get $ a_{0} = \frac{1}{20} \int_{-10}^{10}x(t)e^{-j(0)(\frac{2\pi}{20})t}dt $. We know that x(t) = 0 except for -5 < t < 5 where it is 1.
$ a_{0} = \frac{1}{20} \int_{-5}^{5}(1)e^{(0)}dt = \frac{1}{20}x \bigg|_{-5}^{5} = \frac{1}{2} $
$ a_{k} = \frac{1}{20}\int_{-5}^{5}(1)e^{-jk(\frac{2\pi}{20})t}dt; \text{ where } -5 < k <5 \text{ and }k \neq 0 $
$ a_{k} = \frac{1}{20} \left[ \frac{e^{-jk(\frac{\pi}{10})t}}{-jk(\frac{\pi}{10})}\right]_{-5}^{5} $
$ a_{k} = \frac{1}{20}\left(\frac{1}{-jk\frac{\pi}{10}}\right) \left[ e^{-jk(\frac{\pi}{10})5} - e^{-jk(\frac{\pi}{10})(-5)} \right] $
$ a_{k}= \frac{-1}{2jk}\left[ e^{-\frac{jk\pi}{2}} - e^{\frac{jk\pi}{2}} \right]\text{ for }-5 < k < 5\text{ and }k \neq 0\text{, all others }0 $
$ x(t) = \sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty}a_{k}e^{jk\frac{2\pi}{T}t} $
$ x(t) = \sum_{k=-5}^{-5} a_{k}e^{jk\frac{ \pi}{10}t} $ I changed the limits of the sum because $ a_{k} $ is 0 for anything outside that range.
Answer 3
Write it here.

