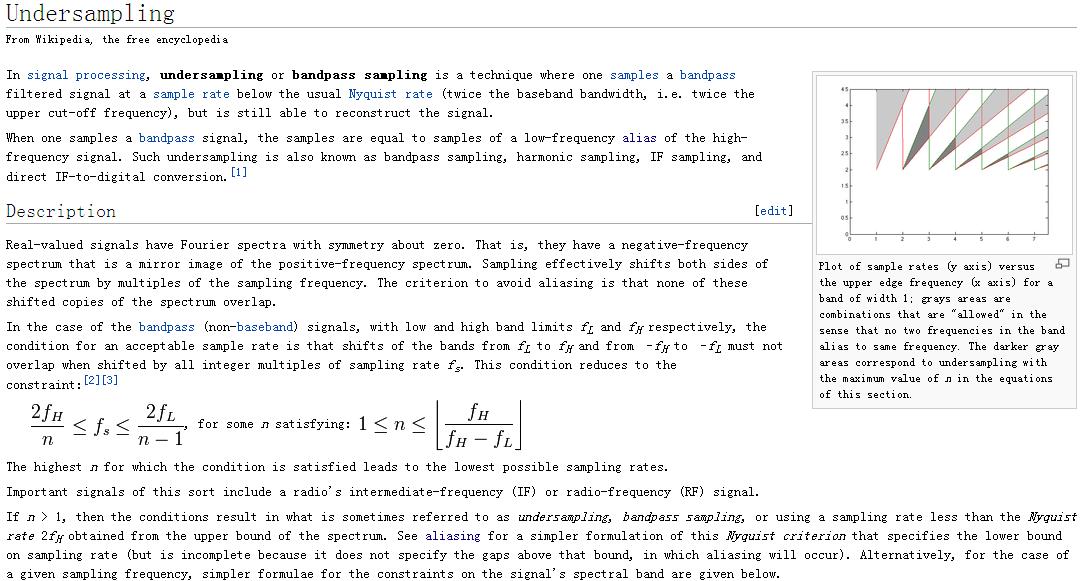
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | Discussion about this page: | ||
| + | *I do not see the point of "copying and pasting" the content of other websites (e.g., wikipedia) on Rhea. If you are interested in writing a page about sampling, why don't you actually write it yourself? -pm | ||
| + | *Is the image you posted below is copyrighted? | ||
| + | ---- | ||
Sampling is the basis of A/D conversion. A continuous time signal(analog) is consisted of infinite data points and it is impossible to process infinite data points. So, A/D converter sample enough points to represent the continuous signal and form discrete signal(Digital). | Sampling is the basis of A/D conversion. A continuous time signal(analog) is consisted of infinite data points and it is impossible to process infinite data points. So, A/D converter sample enough points to represent the continuous signal and form discrete signal(Digital). | ||
Revision as of 17:00, 3 December 2010
Discussion about this page:
- I do not see the point of "copying and pasting" the content of other websites (e.g., wikipedia) on Rhea. If you are interested in writing a page about sampling, why don't you actually write it yourself? -pm
- Is the image you posted below is copyrighted?
Sampling is the basis of A/D conversion. A continuous time signal(analog) is consisted of infinite data points and it is impossible to process infinite data points. So, A/D converter sample enough points to represent the continuous signal and form discrete signal(Digital).
Very simple model for sampling
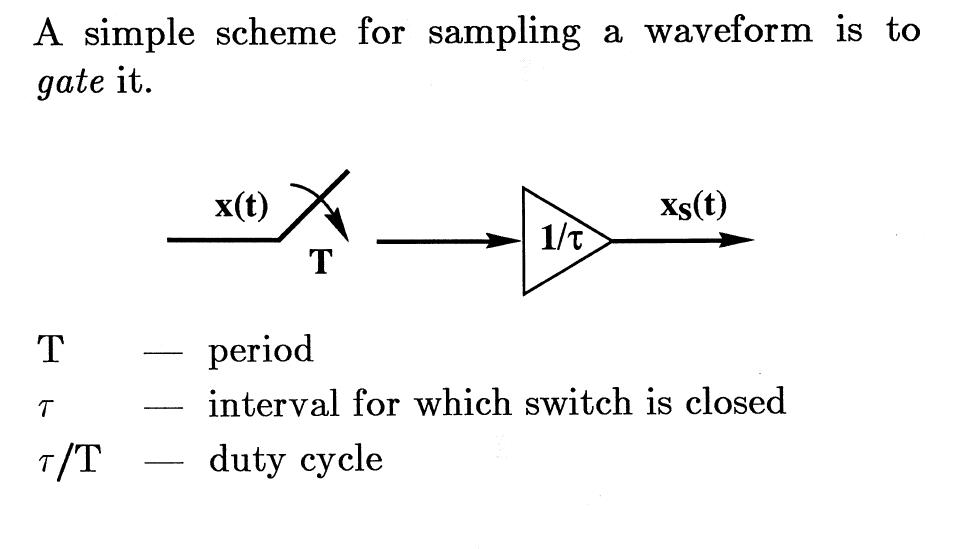 File:Page7.jpg
File:Page7.jpg
References
^ Walt Kester (2003). Mixed-signal and DSP design techniques. Newnes. p. 20. ISBN 9780750676113. ^ Hiroshi Harada, Ramjee Prasad (2002). Simulation and Software Radio for Mobile Communications. Artech House. ISBN 1580530443. ^ Angelo Ricotta. "Undersampling SODAR Signals".