Aliasing is what occurs when a signal is not able to be completely reconstructed due to an insufficient sampling rate. This phenomenon may occur if the sampling frequency is below what is known as the Nyquist Frequency. The Nyquist Frequency can be expressed as: $ F_n = F_s*2 $ where $ F_s $ is the highest frequency in the signal.
To show some of the dangers of aliasing here are some examples.
Example 1: Say you have the signal $ x(t)= \cos(2*\Pi*50t) $
Then the Nyquist Frequency would be $ 2*50Hz = 100Hz $
If we sample at 200 Hz, the sampled signal would be
$ x[n] = x(nT)=x(\frac{n}{75})=\cos(\frac{2*\pi*50*n}{200}) $
with a transform of
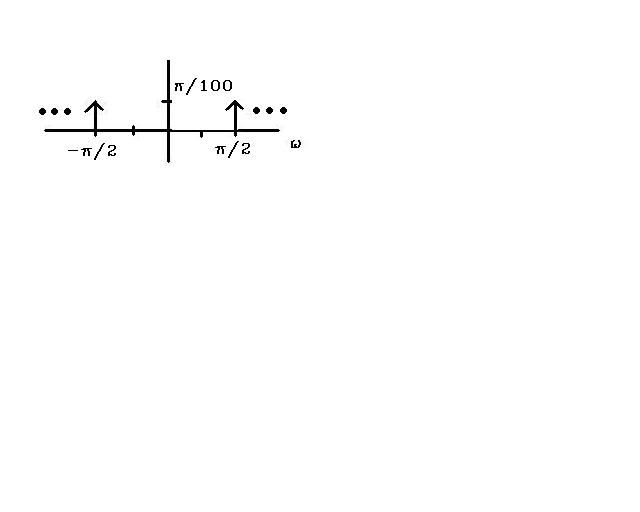
$ \mathfrak{F}(\omega)=\sum_{n=-\infty}^{\infty}x[n]*e^{-jn\omega} $
This would look like
If we sampled the signal at over 100Hz then there would be no threat of aliasing, but let's see what happens when we sample at 75Hz.
At 75Hz, $ T_s=\frac{1}{75}s $
Then, $ x[n] = x(nT)=x(\frac{n}{75})=\cos(\frac{2*\pi*50*n}{75}) $
$ \mathfrak{F}(\omega)=\sum_{n=-\infty}^{\infty}x[n]*e^{-jn\omega} $
While sampling above the Nyquist Frequency will eliminate aliasing it is possible to sample below it and still not get aliasing, however this depends on the signal itself and is not recommended for general sampling.