(→Lectures) |
|||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
[http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_1_-_Introduction 1] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_2_-_Decision_Hypersurfaces 2] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_3_-_Bayes_classification 3] | [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_1_-_Introduction 1] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_2_-_Decision_Hypersurfaces 2] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_3_-_Bayes_classification 3] | ||
[http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_4_-_Bayes_Classification 4] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_5_-_Discriminant_Functions 5] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_6_-_Discriminant_Functions 6] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_7_-_MLE_and_BPE 7] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_8_-_MLE%2C_BPE_and_Linear_Discriminant_Functions 8] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_9_-_Linear_Discriminant_Functions 9] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_10_-_Batch_Perceptron_and_Fisher_Linear_Discriminant 10] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_11_-_Fischer%27s_Linear_Discriminant_again 11] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_12_-_Support_Vector_Machine_and_Quadratic_Optimization_Problem 12] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_13_-_Kernel_function_for_SVMs_and_ANNs_introduction 13] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_14_-_ANNs%2C_Non-parametric_Density_Estimation_%28Parzen_Window%29 14] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_15_-_Parzen_Window_Method 15] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_16_-_Parzen_Window_Method_and_K-nearest_Neighbor_Density_Estimate 16] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_17_-_Nearest_Neighbors_Clarification_Rule_and_Metrics 17] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_18_-_Nearest_Neighbors_Clarification_Rule_and_Metrics%28Continued%29 18] | [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_4_-_Bayes_Classification 4] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_5_-_Discriminant_Functions 5] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_6_-_Discriminant_Functions 6] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_7_-_MLE_and_BPE 7] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_8_-_MLE%2C_BPE_and_Linear_Discriminant_Functions 8] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_9_-_Linear_Discriminant_Functions 9] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_10_-_Batch_Perceptron_and_Fisher_Linear_Discriminant 10] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_11_-_Fischer%27s_Linear_Discriminant_again 11] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_12_-_Support_Vector_Machine_and_Quadratic_Optimization_Problem 12] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_13_-_Kernel_function_for_SVMs_and_ANNs_introduction 13] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_14_-_ANNs%2C_Non-parametric_Density_Estimation_%28Parzen_Window%29 14] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_15_-_Parzen_Window_Method 15] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_16_-_Parzen_Window_Method_and_K-nearest_Neighbor_Density_Estimate 16] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_17_-_Nearest_Neighbors_Clarification_Rule_and_Metrics 17] [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_18_-_Nearest_Neighbors_Clarification_Rule_and_Metrics%28Continued%29 18] | ||
| + | [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_19_-_Nearest_Neighbor_Error_Rates 19] | ||
| + | [http://balthier.ecn.purdue.edu/index.php/Lecture_20_-_Density_Estimation_using_Series_Expansion_and_Decision_Trees 20] | ||
Revision as of 15:18, 28 March 2008
Density Estimation using Series Expansion
Last "non-parametric" technique (although very parametric)
Write $ p(x) = sum(cj*fj(x)) $ where {$ fj's $} are pre-determined class of functions $ =sum(cj*fj(x)) $
Monomials. E.g. Taylor expansion about Xo in 1-D.
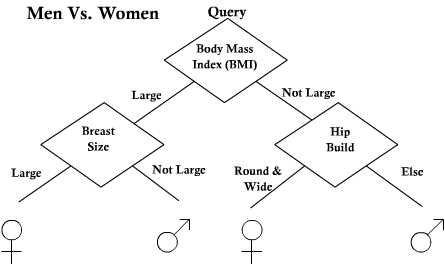
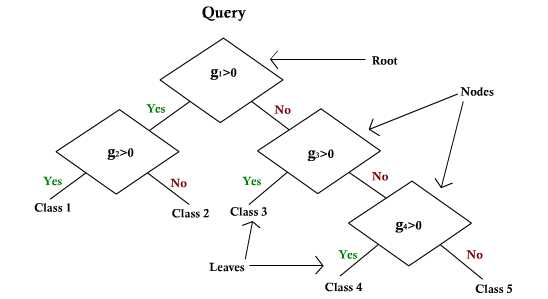
Decision Trees
Reference DHS Chapter 8
Instead of asking a complicated question $ g(x) >= 0 or <0 $
The idea: Ask a series of simple questions following a tree structure (linear 1-D).