(→Time Invariance) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Time Invariance == | == Time Invariance == | ||
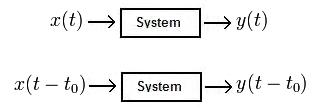
| − | A system is time-invariant if | + | A system is time-invariant if the input <math>x(t)\!</math> and output <math>y(t)\!</math> then the response from an input <math>x(t-t_0)\!</math> will be <math>y(t-t_0)\!</math>. |
[[Image:Timeinv_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.JPG]] | [[Image:Timeinv_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.JPG]] | ||
| − | |||
== Example of a Time Invariant System == | == Example of a Time Invariant System == | ||
Revision as of 13:09, 11 September 2008
Time Invariance
A system is time-invariant if the input $ x(t)\! $ and output $ y(t)\! $ then the response from an input $ x(t-t_0)\! $ will be $ y(t-t_0)\! $.
Example of a Time Invariant System
Let $ y(t)=2x(t)+2\! $. The system is time invarient if for input $ y(t)=2x(t-t_0)+2\! $ the response is $ y(t)=2x(t)+2\! $.