(New page: == Linear Systems == <math>x_1(t) y_1(t) x_2(t) y_2(t) a b \!</math>) |
|||
| (16 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[Homework 2_ECE301Fall2008mboutin]] - [[HW2-A Phil Cannon_ECE301Fall2008mboutin|'''A''']] - [[HW2-B Phil Cannon_ECE301Fall2008mboutin|'''B''']] - [[HW2-C Phil Cannon_ECE301Fall2008mboutin|'''C''']] - [[HW2-D Phil Cannon_ECE301Fall2008mboutin|'''D''']] - [[HW2-E Phil Cannon_ECE301Fall2008mboutin|'''E''']] | ||
| + | |||
== Linear Systems == | == Linear Systems == | ||
| − | <math> | + | Because we are engineers we will use a picture to describe a linear system: |
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Systempjcannon3_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.JPG]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Where <math>a \!</math> and <math>b\!</math> are real or complex. The system is defined as linear if <math>z(t)=w(t)\!</math> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | In other words, if in one scenario we have two signals put into a system, multiplied by a variable, then summed together, the output should equal the output of a second scenario where the signals are multiplied by a variable, summed together, then put through the same system. If this is true, then the system is defined as linear. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Example of a Linear System == | ||
| + | Let <math>y(t)=x(t) \!</math>. Then: | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [[Image:Linsystempjcannon_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.JPG]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Thus, the system <math>y(t)=x(t)\!</math> is linear. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Example of a Non-Linear System == | ||
| + | Let <math>y(t)=x^2(t) \!</math>. Then: | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [[Image:Nonlinsystempjcannon2_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.JPG]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Thus, the system <math>y(t)=x^2(t)\!</math> is non-linear. | ||
Latest revision as of 17:05, 11 September 2008
Homework 2_ECE301Fall2008mboutin - A - B - C - D - E
Linear Systems
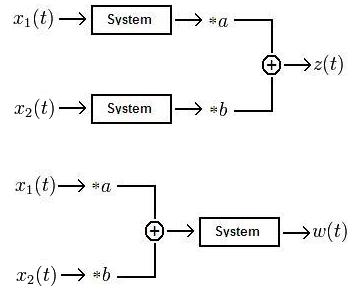
Because we are engineers we will use a picture to describe a linear system:
Where $ a \! $ and $ b\! $ are real or complex. The system is defined as linear if $ z(t)=w(t)\! $
In other words, if in one scenario we have two signals put into a system, multiplied by a variable, then summed together, the output should equal the output of a second scenario where the signals are multiplied by a variable, summed together, then put through the same system. If this is true, then the system is defined as linear.
Example of a Linear System
Let $ y(t)=x(t) \! $. Then:
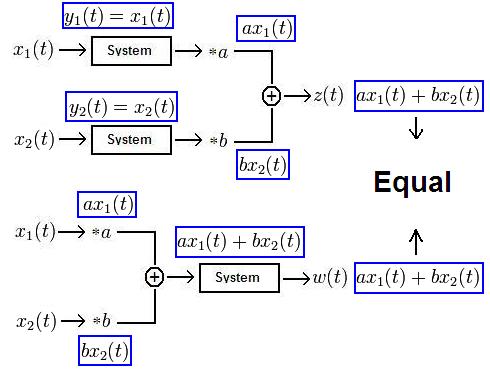
Thus, the system $ y(t)=x(t)\! $ is linear.
Example of a Non-Linear System
Let $ y(t)=x^2(t) \! $. Then:
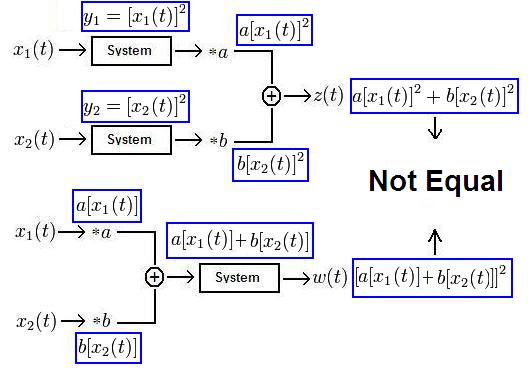
Thus, the system $ y(t)=x^2(t)\! $ is non-linear.