(→Part 1) |
(→Part 1) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
Given the Signal <math>y=cos(pi*t)</math>, One can make 2 DT Signals one that is periodic and one that is nonperiodic. | Given the Signal <math>y=cos(pi*t)</math>, One can make 2 DT Signals one that is periodic and one that is nonperiodic. | ||
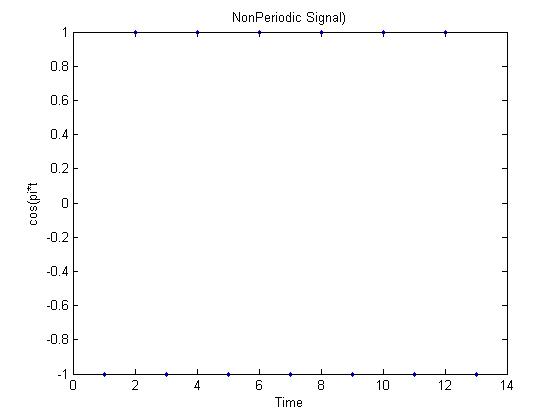
Lets say the Sampling rate is 1. Then the Signal is non periodic as seen in the diagram below. | Lets say the Sampling rate is 1. Then the Signal is non periodic as seen in the diagram below. | ||
| − | <pre> | + | </pre> |
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Nonper_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.jpg]] |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
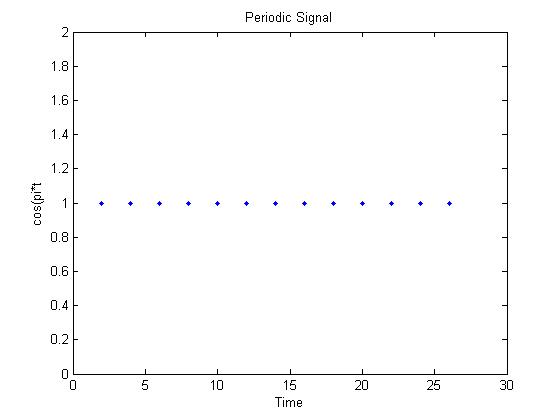
If the sampling frequency is 2 then the Signal is periodic as seen below. | If the sampling frequency is 2 then the Signal is periodic as seen below. | ||
| − | <pre> | + | </pre> |
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Per_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.jpg]] |
== MATLAB CODE == | == MATLAB CODE == | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
plot(t,y,'.') | plot(t,y,'.') | ||
xlabel('Time') | xlabel('Time') | ||
| − | ylabel('cos(pi*t') | + | ylabel('cos(pi*t)') |
title('NonPeriodic Signal)') | title('NonPeriodic Signal)') | ||
t=t.*(2) | t=t.*(2) | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
title('NonPeriodic Signal)') | title('NonPeriodic Signal)') | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
== Part 2 == | == Part 2 == | ||
Revision as of 17:58, 10 September 2008
Part 1
Given the Signal <math>y=cos(pi*t)</math>, One can make 2 DT Signals one that is periodic and one that is nonperiodic. Lets say the Sampling rate is 1. Then the Signal is non periodic as seen in the diagram below.
If the sampling frequency is 2 then the Signal is periodic as seen below.
MATLAB CODE
t=[1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13]
y=cos(pi.*t)
figure(1)
plot(t,y,'.')
xlabel('Time')
ylabel('cos(pi*t)')
title('NonPeriodic Signal)')
t=t.*(2)
y=cos(pi.*t)
figure(2)
plot(t,y,'.')
xlabel('Time')
ylabel('cos(pi*t')
title('NonPeriodic Signal)')