(New page: The CT signal <math>\cos{x}</math> can be both periodic and non-periodic in DT. With a sampling rate of <math>1</math> the DT signal looks like this: and is non-periodic. With a sampl...) |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
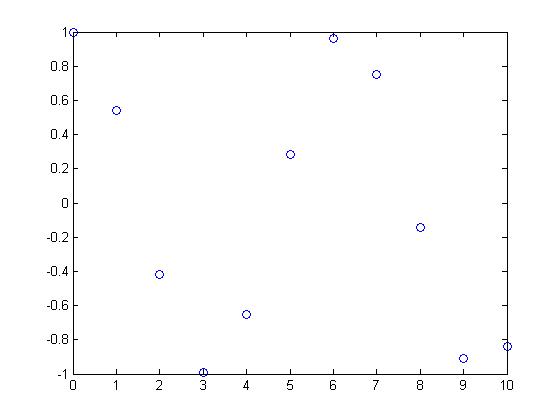
With a sampling rate of <math>1</math> the DT signal looks like this: | With a sampling rate of <math>1</math> the DT signal looks like this: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Nonperiodic_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.jpg]] | ||
and is non-periodic. | and is non-periodic. | ||
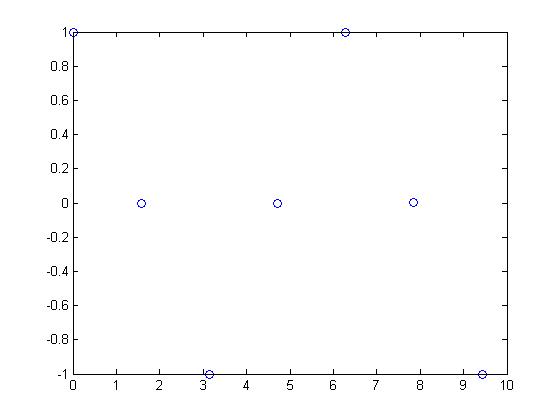
With a sampling rate of <math>\frac{\pi}{2}</math> the DT signal looks like this: | With a sampling rate of <math>\frac{\pi}{2}</math> the DT signal looks like this: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Periodic2_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.jpg]] | ||
and is periodic. | and is periodic. | ||
Latest revision as of 04:13, 12 September 2008
The CT signal $ \cos{x} $ can be both periodic and non-periodic in DT.
With a sampling rate of $ 1 $ the DT signal looks like this:
and is non-periodic.
With a sampling rate of $ \frac{\pi}{2} $ the DT signal looks like this:
and is periodic.