(→Part 1) |
(→Part 2) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | ===Periodic Signals Revisited=== | ||
==Part 1== | ==Part 1== | ||
Choosing the CT periodic function <math>sin(x)</math> the frequency is 0.1 | Choosing the CT periodic function <math>sin(x)</math> the frequency is 0.1 | ||
| Line 5: | Line 6: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | The DC signal at this frequency would be: | + | The periodic DC signal at this frequency would be: |
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Hw2-1-2_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.jpg]] |
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | The non-periodic DC signal with frequency @ 0.6 | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [[Image:Hw2-1-3_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Part 2== | ||
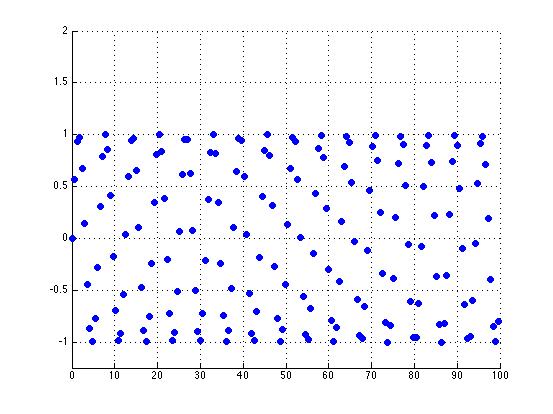
| + | Choosing the non-periodic function <math>y=x</math> and making it periodic: | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [[Image:Hw-2.jpg_ECE301Fall2008mboutin]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:12, 12 September 2008
Periodic Signals Revisited
Part 1
Choosing the CT periodic function $ sin(x) $ the frequency is 0.1
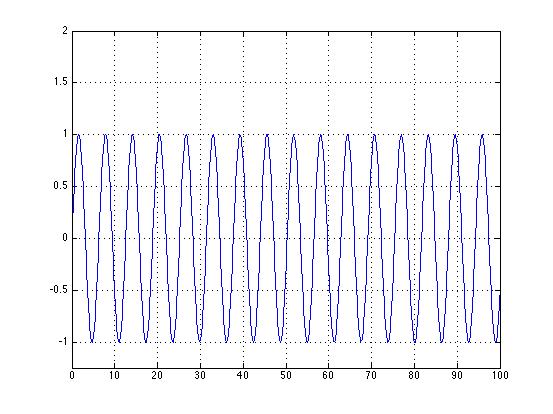
The periodic DC signal at this frequency would be:
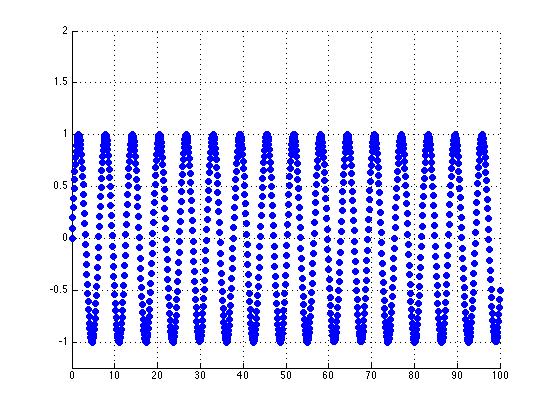
The non-periodic DC signal with frequency @ 0.6
Part 2
Choosing the non-periodic function $ y=x $ and making it periodic:
File:Hw-2.jpg ECE301Fall2008mboutin

