| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Periodic Functions== | ==Periodic Functions== | ||
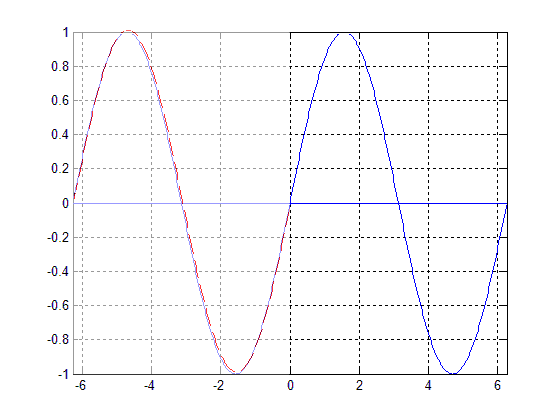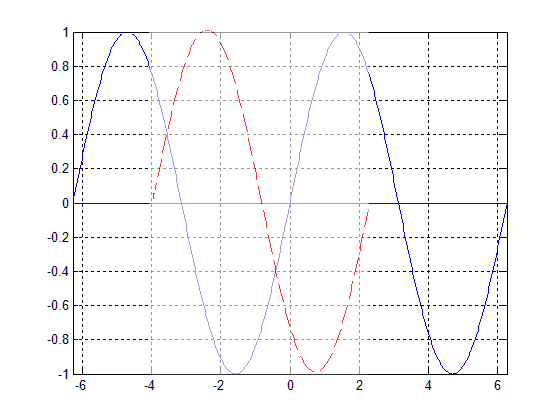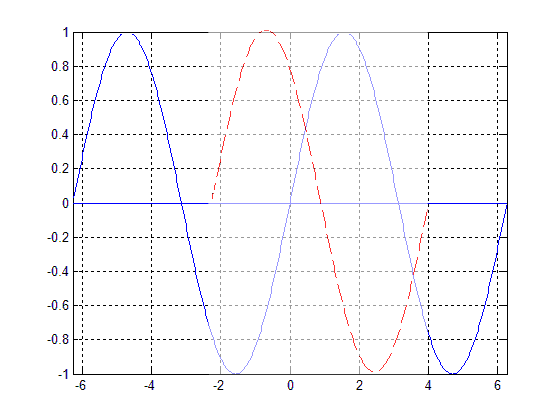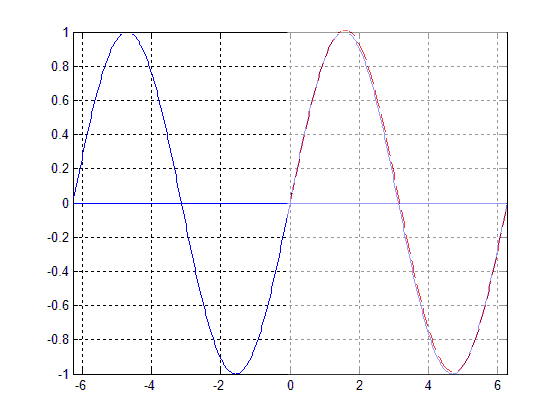
| − | The function <math>f(t)=sin(t | + | The function <math>f(t)=sin(t-T)</math> is periodic, with a period of <math>T=2\pi</math>. This means that for <math>T=2n\pi</math>, n an integer, the function will be unchanged from when <math>T=0</math>. |
| − | [[Image:Periodic_blaskows_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.gif|frame|center|An example of a periodic function <math>f(t)=sin(t | + | [[Image:Periodic_blaskows_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.gif|frame|center|An example of a periodic function <math>f(t)=sin(t-T)</math>. The dashed red line represents various values of <math>T</math> from <math>T=0</math> to <math>T=2\pi</math>. One can see that when <math>T=2\pi</math>, the function is unchanged.]] |
==Non-periodic Functions== | ==Non-periodic Functions== | ||
Revision as of 06:46, 2 September 2008
Periodic Functions
The function $ f(t)=sin(t-T) $ is periodic, with a period of $ T=2\pi $. This means that for $ T=2n\pi $, n an integer, the function will be unchanged from when $ T=0 $.
Non-periodic Functions
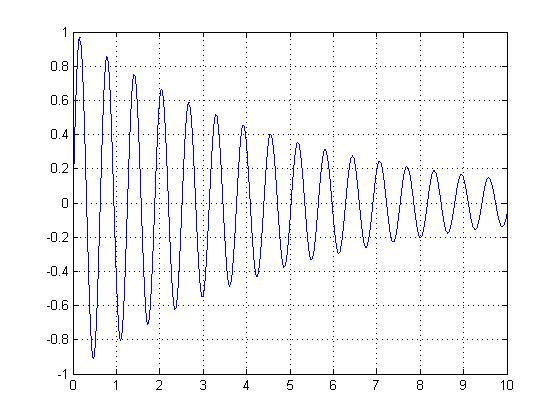
A non-periodic function does not remain self-similar for all integer multiples of its period. A decaying exponential is an example of a non-periodic function. The distance between consecutive peaks does not remain constant for all values of $ x $. Presented here is the function $ f(t)=e^{0.2t}*sin(10t) $.