(New page: Complex Numbers) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Complex Numbers | Complex Numbers | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Definition''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:ComplexNumberArgand_1000_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.gif]] | ||
| + | |||
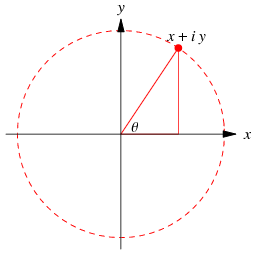
| + | The complex numbers are the field C of numbers of the form x+iy, where x and y are real numbers and i is the imaginary unit equal to the square root of -1, sqrt(-1). | ||
| + | A complex number can be visually represented as a pair of numbers forming a vector on a diagram | ||
| + | A complex number can be visually represented as a pair of numbers forming a vector on a diagram | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Operations''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Complex numbers are added, subtracted, multiplied, and divided by formally applying the associative, commutative and distributive laws of algebra, together with the equation i 2 = −1: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Addition: [[Image:1_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.png]] | ||
| + | * Subtraction: [[Image:2_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.png]] | ||
| + | * Multiplication: [[Image:3_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.png]] | ||
| + | * Division: [[Image:4_ECE301Fall2008mboutin.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | where c and d are not both zero. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is also possible to represent complex numbers as ordered pairs of real numbers, so that the complex number a + ib corresponds to (a, b). In this representation, the algebraic operations have the following formulas: | ||
| + | |||
| + | (a, b) + (c, d) = (a + c, b + d) | ||
| + | (a, b)(c, d) = (ac − bd, bc + ad) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Since the complex number a + bi is uniquely specified by the ordered pair (a, b), the complex numbers are in one-to-one correspondence with points on a plane. This complex plane is described below. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sources : wikipedia | ||
Latest revision as of 15:43, 4 September 2008
Complex Numbers
Definition
The complex numbers are the field C of numbers of the form x+iy, where x and y are real numbers and i is the imaginary unit equal to the square root of -1, sqrt(-1). A complex number can be visually represented as a pair of numbers forming a vector on a diagram A complex number can be visually represented as a pair of numbers forming a vector on a diagram
Operations
Complex numbers are added, subtracted, multiplied, and divided by formally applying the associative, commutative and distributive laws of algebra, together with the equation i 2 = −1:
* Addition:* Subtraction:
* Multiplication:
* Division:
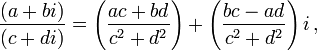
where c and d are not both zero.
It is also possible to represent complex numbers as ordered pairs of real numbers, so that the complex number a + ib corresponds to (a, b). In this representation, the algebraic operations have the following formulas:
(a, b) + (c, d) = (a + c, b + d) (a, b)(c, d) = (ac − bd, bc + ad)
Since the complex number a + bi is uniquely specified by the ordered pair (a, b), the complex numbers are in one-to-one correspondence with points on a plane. This complex plane is described below.
Sources : wikipedia