(New page: Category:2010 Fall ECE 438 Boutin ---- == Solution to Question 1 of HW5 == ---- <math>x_r(t)= \sum_{k=-\infty}^\infty x(kT) \text{ sinc} \left(\frac{t-kT}{T}\right)</math> Let m be...) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
<math>\begin{align} | <math>\begin{align} | ||
Y(w) &= \sum_{n=-\infty}^{\infty} y[n]e^{-jwn} = \sum_{n=-\infty}^{\infty} x[3n]e^{-jwn} \\ | Y(w) &= \sum_{n=-\infty}^{\infty} y[n]e^{-jwn} = \sum_{n=-\infty}^{\infty} x[3n]e^{-jwn} \\ | ||
| − | &= \sum_{m=-\infty, m= | + | &= \sum_{m=-\infty, m=Dk}^{\infty} x[m]e^{-j\frac{wm}{D}} = \sum_{m=-\infty}^{\infty} x[m] \left( \sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty} \delta[m-Dk] \right) e^{-j\frac{wm}{D}} \\ |
| − | &= \sum_{m=-\infty}^{\infty} x[m] \left( \frac{1}{D} \sum_{k=0}^{D-1} e^{j\frac{2\pi}{D} | + | &= \sum_{m=-\infty}^{\infty} x[m] \left( \frac{1}{D} \sum_{k=0}^{D-1} e^{j\frac{2\pi}{D}km} \right) e^{-j\frac{wm}{D}} = \sum_{k=0}^{D-1} \frac{1}{D} \sum_{m=-\infty}^{\infty} x[m]e^{j\left(w-\frac{2\pi}{D}k\right)m} \\ |
&= \sum_{k=0}^{D-1} \frac{1}{D} X\left(\frac{w-2\pi k}{D}\right) \\ | &= \sum_{k=0}^{D-1} \frac{1}{D} X\left(\frac{w-2\pi k}{D}\right) \\ | ||
\end{align}</math> | \end{align}</math> | ||
Latest revision as of 04:56, 2 October 2011
Solution to Question 1 of HW5
$ x_r(t)= \sum_{k=-\infty}^\infty x(kT) \text{ sinc} \left(\frac{t-kT}{T}\right) $
Let m be any integer.
$ \begin{align} \text{a)} \;\; x_r(mT) & = \sum_{k=-\infty}^\infty x(kT) \text{ sinc} \left(\frac{mT-kT}{T}\right) = \sum_{k=-\infty}^\infty x(kT) \text{ sinc} \left((m-k)\right) \\ & = x(mT), \;\; \text{ since} \; \text{ sinc}\left( (m-k) \right) = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} 1 & \text{ when } m=k \\ 0 & \text{ when } m \neq k \end{array} \right. \end{align} $
$ \begin{align} \text{b)} \;\; & \text{The above expression is equivalent to the following:} \\ & x_r(t) = \sum_{k=-\infty}^\infty x(kT) \delta(t-kT) \ast \text{ sinc} \left(\frac{t}{T}\right) \\ \end{align} $
This implies that the reconstructed signal $ x_r(t) $ is the output of a filter when we input the impulse train of $ x(t) $ with period $ T $.
The impulse response of this filter is $ \text{sinc}(t/T) $, whose frequency response is a ideal low-pass filter with the cut-off frequency of $ 1/(2T) $.
Thus the signal bandwidth $ B $ must be less than $ 1/(2T) $ for the perfect reconstruction.
But the sampling frequency for the impulse train was $ F_s=1/T $. Thus the sampling frequency must be larger than $ 2B $, in order to avoid aliasing when reconstruction.
Hence, when $ F_s>2B $, $ x_r(t)=x(t) $.
Solution to Question 2 of HW5
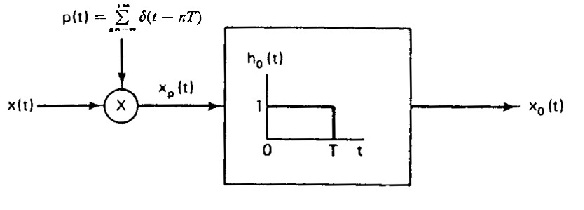
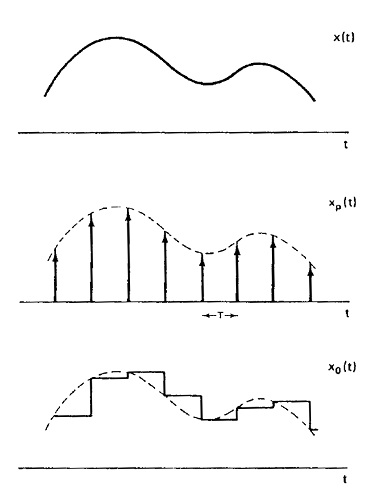
$ \begin{align} \text{a)} \;\; & x_p(t)=x(t) \sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty} \delta(t-kT) = \sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty} x(kT) \delta(t-kT) \\ & h_0(t) = \text{rect}\left(\frac{t-\frac{T}{2}}{T}\right) \\ & x_0(t) = x_p(t) \ast h_0(t) = \sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty} x(kT) \delta(t-kT) \ast \text{rect}\left(\frac{t-\frac{T}{2}}{T}\right) = \sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty} x(kT) \text{rect}\left(\frac{t-(k+\frac{1}{2})T}{T}\right) \\ \end{align} $
$ \text{b)}\,\! $
$ \text{c)} \;\; \text{There is no such condition and the impulse response of this LTI system is } h_0(t)\,\! $.
$ \text{d)} \;\; \text{False} \,\! $
Even though the signal is band-limited, sampling will incur the replicas at every multiples of sampling frequency $ 1/T $.
And the frequency response of zero-order hold is $ H_0(e^{jw})=T\text{ sinc}(wT/2)e^{-jwT/2} $, which is not like a low-pass filter.
Therefore, the frequency response of $ x_0(t) $ is not band-limited.
Solution to Question 3 of HW5
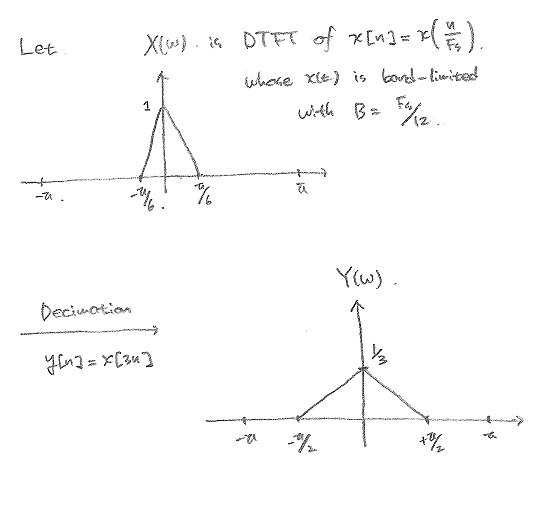
$ \text{a)} \;\; \text{General Relation for the decimation with a factor of } D \,\! $.
$ \text{Let } X(w) = \mathcal{F}(x[n]) $
$ \begin{align} Y(w) &= \sum_{n=-\infty}^{\infty} y[n]e^{-jwn} = \sum_{n=-\infty}^{\infty} x[3n]e^{-jwn} \\ &= \sum_{m=-\infty, m=Dk}^{\infty} x[m]e^{-j\frac{wm}{D}} = \sum_{m=-\infty}^{\infty} x[m] \left( \sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty} \delta[m-Dk] \right) e^{-j\frac{wm}{D}} \\ &= \sum_{m=-\infty}^{\infty} x[m] \left( \frac{1}{D} \sum_{k=0}^{D-1} e^{j\frac{2\pi}{D}km} \right) e^{-j\frac{wm}{D}} = \sum_{k=0}^{D-1} \frac{1}{D} \sum_{m=-\infty}^{\infty} x[m]e^{j\left(w-\frac{2\pi}{D}k\right)m} \\ &= \sum_{k=0}^{D-1} \frac{1}{D} X\left(\frac{w-2\pi k}{D}\right) \\ \end{align} $
Replacing D with 3 would be the answer.
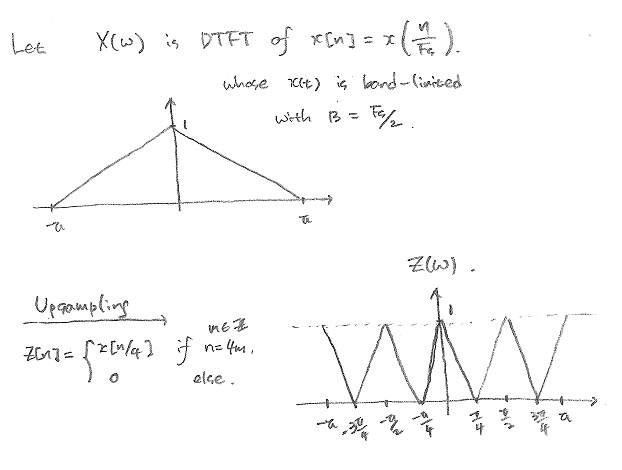
$ \text{b)} \;\; \text{General Relation for the upsampling with a factor of } L \,\! $.
$ \begin{align} Z(w) &= \sum_{n=-\infty}^{\infty} z[n]e^{-jwn} \\ &= \sum_{n=-\infty}^{\infty} \left( \sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty} x[k] \delta[n-kL] \right) e^{-jwn} \\ &= \sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty} x[k] \sum_{n=-\infty}^{\infty} \delta[n-kL] e^{-jwn} = \sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty} x[k] e^{-jwkL} \\ &= \sum_{k=-\infty}^{\infty} x[k] e^{-jLwk} = X(Lw) \\ &\end{align} $
Since $ X(w) $ is periodic with $ 2\pi $, $ Z(w)=X(Lw) $ is periodic with $ 2\pi/L $.
Replaing L with 4 would be the answer.
Back to HW5
Back to ECE 438 Fall 2010