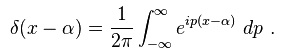| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:ECE301Spring2013JVK]] [[Category:ECE]] [[Category:ECE301]] [[Category:signalandsystems]] [[Category:problem solving]] | [[Category:ECE301Spring2013JVK]] [[Category:ECE]] [[Category:ECE301]] [[Category:signalandsystems]] [[Category:problem solving]] | ||
[[Category:Impulse Response]] | [[Category:Impulse Response]] | ||
| − | '''1.Impulse response'''< | + | '''1.Impulse response'''<\n> |
| − | Joseph Fourier first represented Fourier integral theorem in the following DOE:< | + | Joseph Fourier first represented Fourier integral theorem in the following DOE:<\n> |
[[Image:DOE1.jpg]][1] | [[Image:DOE1.jpg]][1] | ||
| − | Which is then introduced into the first delta function as following:< | + | Which is then introduced into the first delta function as following:<\n> |
[[Image:DOE2.jpg]][1] | [[Image:DOE2.jpg]][1] | ||
| − | And the end end up with what mathematicians called Dirac delta function:< | + | And the end end up with what mathematicians called Dirac delta function:<\n> |
[[Image:DOE3.jpg]] [1] | [[Image:DOE3.jpg]] [1] | ||
Revision as of 11:29, 11 March 2013
1.Impulse response<\n>
Joseph Fourier first represented Fourier integral theorem in the following DOE:<\n>
![]() [1]
Which is then introduced into the first delta function as following:<\n>
[1]
Which is then introduced into the first delta function as following:<\n>
![]() [1]
And the end end up with what mathematicians called Dirac delta function:<\n>
[1]
And the end end up with what mathematicians called Dirac delta function:<\n>
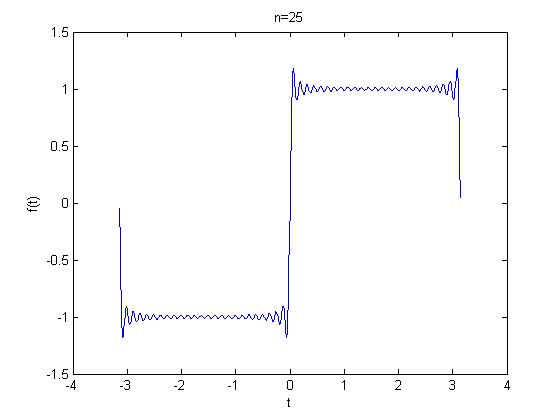
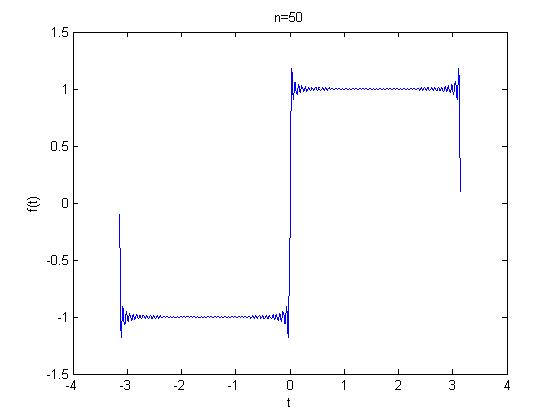
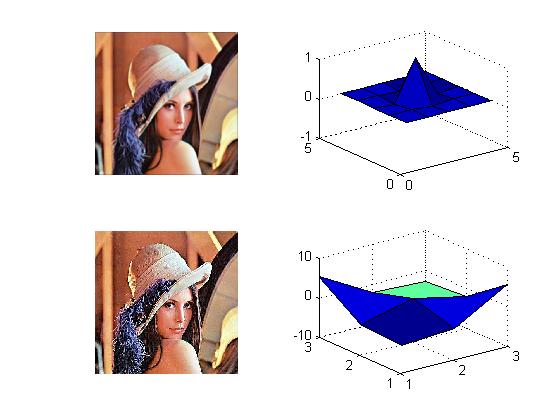
The input x(t) is a function with a fundamental period x(t)= 1 from x= 0 to 1 and f(x)= -1 to 0, with a discontinuity at x=0. The following graphs from matlab represents Gibbs phenomena, as n increases the overshot decreases.
The upper is the Gaussian filter, while bottom is the unsharp.