| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
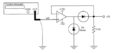
| − | File:square_circuit. | + | File:square_circuit.png|circuit |
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
For example, we set s(t) to be square wave with A = 3V, T0 = 0.5*10^-6s | For example, we set s(t) to be square wave with A = 3V, T0 = 0.5*10^-6s | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File:square_wave.png|s(t) | ||
| + | |||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
The frequency domain of output shown in spectrum analyzer will be: | The frequency domain of output shown in spectrum analyzer will be: | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File:frequency_time_domain.jpg|freq_domain | ||
| + | |||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
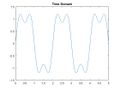
The time domain of output shown in oscilloscope will be: | The time domain of output shown in oscilloscope will be: | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File:output_time_domain.png|time_domain | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
Revision as of 16:42, 21 April 2018
Approximating Periodic Signals with Finite Fourier Series
In this project, a matlab function will be used to show how a finite number of Fourier Series coefficients can approximate a periodic signal.
When there are only 1 non-zero term, the time and frequency domain are shown below:
When 2 non-zero terms
When 5 non-zeros terms
When there are 25 non-zero terms
Conclusion: From the above diagrams we are able to distinguish that: As the number of Fourier Series Coefficients increases, the output of approximated periodic signal is more accurate.
A circuit is built to measure the Fourier series of a Square wave
For example, we set s(t) to be square wave with A = 3V, T0 = 0.5*10^-6s
The frequency domain of output shown in spectrum analyzer will be:
- Frequency time domain.jpg
freq_domain
The time domain of output shown in oscilloscope will be: