| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
'''Internal structure of DES''' | '''Internal structure of DES''' | ||
| − | + | 1. Initial Permutaion(IP) : This is the first thing that is seen in the expanded view of DES block in Fig 1. | |
** IP is a bitwise permutation or simple crosswiring in hardware. | ** IP is a bitwise permutation or simple crosswiring in hardware. | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
[[File:IPFP.png|500px|thumb|left|Fig 2:Initial Permutation and the Final Permutation table ]] | [[File:IPFP.png|500px|thumb|left|Fig 2:Initial Permutation and the Final Permutation table ]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2. DES Encryption Round - Feistel Networks | ||
| − | |||
Revision as of 05:51, 11 June 2015
Data Encryption Standard(DES)
A slecture on Cryptography by student Divya Agarwal and Katie Marsh
Partly based on the Summer 2015 lecture material of Prof. Paar.
Contents
Link to video on youtube
Accompanying Lecture Notes
Introduction
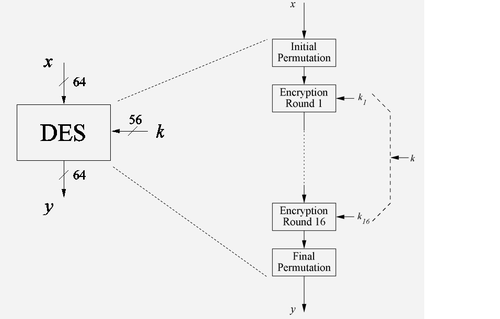
- DES is a block cipher and as the name suggests it works on blocks of bits or binary numbers--the 0s and the 1s common to digital world. It encrypts group of 64 plaintext bits(one block) and returns 64 ciphertext bits. To do the encryption, DES uses keys which are also 64 bits long. However, every 8th key bit is ignored in the DES algorithm, so that the effective key size is 56 bits.
Block Cipher Primitives
- Confusion : An encryption operation where the relationship between plaintext and ciphertext is obscured. Today, a common element for achieving confusion is substitution, which is found in both AES and DES.
- Diffusion : An encryption operation where the influence of one plaintext symbol is spread over many ciphertext symbols with the goal of hiding statistical properties of the plaintext. A simple diffusion element is the bit permutation, which is frequently used within DES.
Both operations by themselves cannot provide security. The idea is to concatenate confusion and diffusion elements to build a more secure cipher.
Overview of DES Algorithm
- DES is a Symmetric cipher: uses same key for encryption and decryption
- Uses 16 rounds which all perform the identical operation
- Different subkey(48 bit) in each round derived from main key
Internal structure of DES
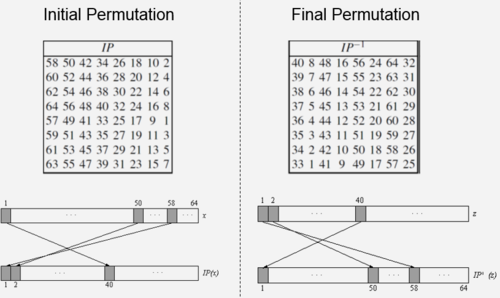
1. Initial Permutaion(IP) : This is the first thing that is seen in the expanded view of DES block in Fig 1.
- IP is a bitwise permutation or simple crosswiring in hardware.
- The corsswiring is done according to the table(left) given in Fig 2.
- The IP has no effect on the DES security at all.
2. DES Encryption Round - Feistel Networks
References
- C. Paar. Understanding Cryptography. Lecture Notes. Dept. of Electr. Eng. and Information Sciences, Ruhr University.
- C. Paar and J. Pelzl. Understanding Cryptography. A textbook for Student and Practitioners. Springer 2010.
Questions and comments
If you have any questions, comments, etc. please post them here.