Contents
Jason Holmes - Design Notebook
Week of Sept. 19 |
|
September 21, 2011 (1.5 hours):
|
|
September 22, 2011 (20 minutes):
|
|
September 23, 2011 (1 hour):
|
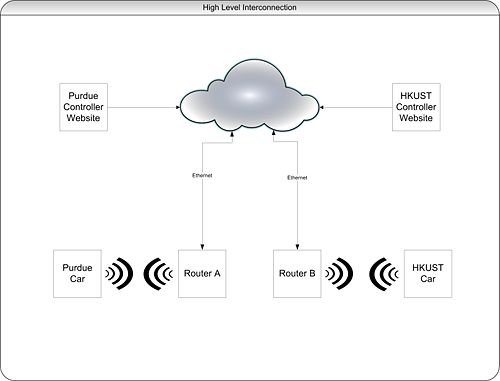
| WEEK SUMMARY: Accomplishments: Obtained usernames for HKUST members
|
Week of Sept. 26 |
|
September 27, 2011 (45 minutes):
|
|
September 27, 2011 (30 minutes):
|
|
September 28, 2011 (1 hour):
|
|
September 29, 2011 (45 minutes):
|
|
September 30, 2011 (1.5 hour):
|
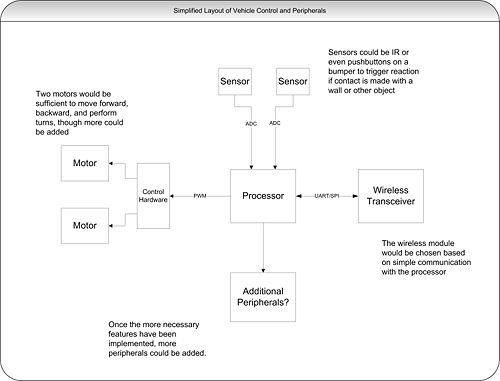
| WEEK SUMMARY: Accomplishments: Completed preliminary block diagram layout of system. Decided on potential processor family.
|
Week of Oct. 3 |
|
October 6, 2011 (2 hours):
|
|
October 7, 2011 (1 hour):
|
|
October 7, 2011 (1.5 hours):
|
| WEEK SUMMARY: Accomplishments: Finished poster for VIP poster session
|
Week of Oct. 10 |
|
October 11, 2011 (30 minutes):
|
|
October 13, 2011 (1 hour):
|
|
October 14, 2011 (1.5 hours):
|
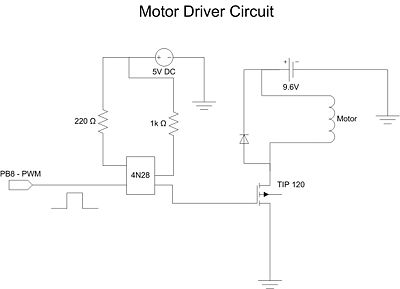
| WEEK SUMMARY: Accomplishments: Decided on a development board to begin prototyping.
|
Week of Oct. 17 |
|
October 17, 2011 (30 minutes):
|
|
October 17, 2011 (1 hour):
|
|
October 18, 2011 (3 hours):
IP Camera:TRENDnet TV-IP110WN Wireless N Internet Camera
|
|
October 19, 2011 (2 hours):
|
|
October 20, 2011 (1 hour):
|
| WEEK SUMMARY: Accomplishments:
|
Week of Oct. 24 |
|
October 25, 2011 (3.2 hours):
(640 x 480 pixels) X (2 bytes per pixel) = 614,400 bytes per frame All of the CMOS cameras output in a RGB format or similar - raw image data. For most cameras, this is 16 bits per pixel. Without doing our own compression, this image data would be impossible to send wirelessly. There is a library for C to convert RGB data to JPEG format, which then possibly be converted to MJPEG on the controller side. This could possibly be used on-board, but the speed would have to be tested.
|
|
October 28, 2011 (1.5 hours):
|
| WEEK SUMMARY: Accomplishments:
|
Week of Oct. 31 |
|
November 1, 2011 (4.5 hours):
|
|
November 3, 2011 (7 hours):
|
|
November 3, 2011 (1.5 hours):
|
| WEEK SUMMARY: Accomplishments: Received tanks
|
Week of Nov. 7 |
|
November 8, 2011 (3 hours):
|
|
November 9, 2011 (3 hours):
|
|
November 10, 2011 (2 hours):
|
|
November 11, 2011 (2 hours):
|
| WEEK SUMMARY: Accomplishments: Completed design review
|
Week of Nov. 14 |
| WEEK SUMMARY: Accomplishments:
|