(New page: Sampling is the basis of A/D conversion. A continuous time signal(analog) is consisted of infinite data points and it is impossible to process infinite data points. So, A/D converter sampl...) |
|||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
[[Image:page6.jpg]] | [[Image:page6.jpg]] | ||
[[Image:page7.jpg]] | [[Image:page7.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | References | ||
| + | |||
| + | ^ Walt Kester (2003). Mixed-signal and DSP design techniques. Newnes. p. 20. ISBN 9780750676113. | ||
| + | ^ Hiroshi Harada, Ramjee Prasad (2002). Simulation and Software Radio for Mobile Communications. Artech House. ISBN 1580530443. | ||
| + | ^ Angelo Ricotta. "Undersampling SODAR Signals". | ||
Revision as of 15:34, 3 December 2010
Sampling is the basis of A/D conversion. A continuous time signal(analog) is consisted of infinite data points and it is impossible to process infinite data points. So, A/D converter sample enough points to represent the continuous signal and form discrete signal(Digital).
Very simple model for sampling
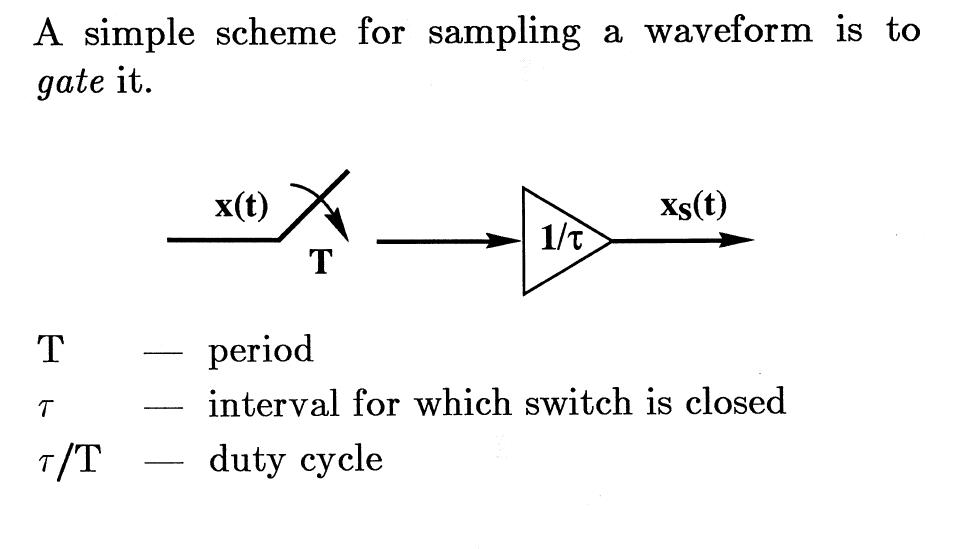 File:Page7.jpg
File:Page7.jpg
References
^ Walt Kester (2003). Mixed-signal and DSP design techniques. Newnes. p. 20. ISBN 9780750676113. ^ Hiroshi Harada, Ramjee Prasad (2002). Simulation and Software Radio for Mobile Communications. Artech House. ISBN 1580530443. ^ Angelo Ricotta. "Undersampling SODAR Signals".