| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | a.<math>x[n]=cos(\frac{\pi n}{2})\text{ ,n=0,1,2,3}</math> | + | a. |
| + | |||
| + | <math>x[n]=cos(\frac{\pi n}{2})\text{ ,n=0,1,2,3}</math> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| Line 24: | Line 26: | ||
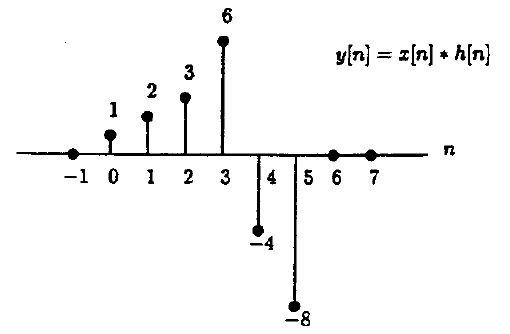
c. Circular convolution equals linear convolution plus aliasing. The length of x[n] is 3 and length of h[n] is 4. We need <math>N\ge 3+4-1=6</math> to avoid aliasing. Since N=4, we expect to get aliasing here. First, find y[n]=x[n]*h[n]: | c. Circular convolution equals linear convolution plus aliasing. The length of x[n] is 3 and length of h[n] is 4. We need <math>N\ge 3+4-1=6</math> to avoid aliasing. Since N=4, we expect to get aliasing here. First, find y[n]=x[n]*h[n]: | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:ECE438_Week12_Quiz_Q5_1.jpg]] |
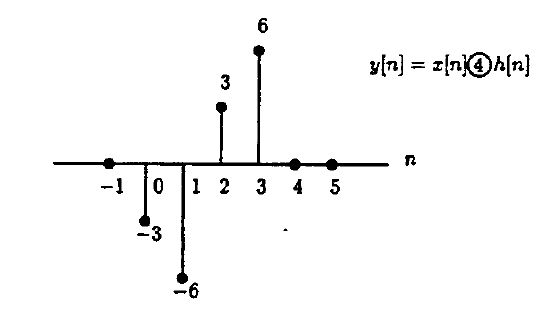
For this problem, aliasing means the last three points (n=4,5,6) will wrap-around on top of the first three points, giving <math>y[n]=x[n]\circledast_4 h[n]</math> | For this problem, aliasing means the last three points (n=4,5,6) will wrap-around on top of the first three points, giving <math>y[n]=x[n]\circledast_4 h[n]</math> | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:ECE438_Week12_Quiz_Q5_2.jpg]] |
d. Using the DFT values we calculated in parts a and b: | d. Using the DFT values we calculated in parts a and b: | ||
Latest revision as of 19:23, 15 November 2010
Solution of Week12 Quiz Question 5
a.
$ x[n]=cos(\frac{\pi n}{2})\text{ ,n=0,1,2,3} $
$ \begin{align} X[k]&=\sum_{n=0}^3 x[n]e^{-j\frac{2\pi n}{N}k} \\ &=\sum_{n=0}^3 cos(\frac{n\pi}{2})e^{-j\frac{2\pi n}{N}k} \\ &=1-e^{-j\pi k}\text{ , }0\le k\le 3 \end{align} $
b. $ h[n]=2^n\text{ ,n=0,1,2,3} $
$ \begin{align} H[k]&=\sum_{n=0}^3 h[n]e^{-j\frac{2\pi n}{N}k} \\ &=\sum_{n=0}^3 2^ne^{-j\frac{2\pi n}{N}k} \\ &=1+2e^{-j\frac{\pi k}{4}}+4e^{-j\pi k}+8e^{-j\frac{3\pi k}{4}}\text{ , }0\le k\le 3 \end{align} $
c. Circular convolution equals linear convolution plus aliasing. The length of x[n] is 3 and length of h[n] is 4. We need $ N\ge 3+4-1=6 $ to avoid aliasing. Since N=4, we expect to get aliasing here. First, find y[n]=x[n]*h[n]:
For this problem, aliasing means the last three points (n=4,5,6) will wrap-around on top of the first three points, giving $ y[n]=x[n]\circledast_4 h[n] $
d. Using the DFT values we calculated in parts a and b:
$ \begin{align} Y[k]&=X[k]H[k] \\ &=1+2e^{-j\frac{\pi k}{4}}+4e^{-j\frac{2\pi k}{4}}+8e^{-j\frac{3\pi k}{4}}-e^{-j\frac{2\pi k}{4}}-2e^{-j\frac{3\pi k}{4}}-4e^{-j\frac{4\pi k}{4}}-8e^{-j\frac{5\pi k}{4}} \\ &=-3-6e^{-j\frac{\pi k}{4}}+3e^{-j\frac{2\pi k}{4}}+6e^{-j\frac{3\pi k}{4}}\text{ , }0\le k\le 3 \end{align} $
Taking the inverse DFT:
$ y[n]=-3\delta [n]-6\delta [n-1]+3\delta [n-2]+6\delta [n-3]\text{ , }0\le n\le 3 $