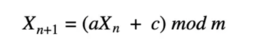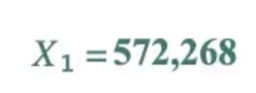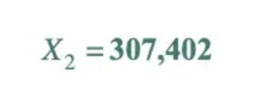| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
===== Middle-Square algorithm ===== | ===== Middle-Square algorithm ===== | ||
| + | |||
A second method of doing pseudo RNG is with a middle square generator. This method takes an input value or seed, and squares it. The resulting number then has its middle digits extracted to be the same length as the original seed, and then this number is used as the next seed. For example, if our initial seed was 3592, we would square it to get 12,902,464. Because our initial seed was 4 digits long, we would drop the 12 at the start and 64 at the end of the number to get our next seed, 9024. This method of RNG does require our squared seed to have twice the number of digits of the initial number, and requires the seed to have an even number of digits. Obviously, there are many numbers that do not follow these rules, so in order to compensate we can add a 0 to the start of a number. In the case of a squared seed not having twice the digits (such as 25*25 = 625), a 0 is added to the squared number to obey the rule (0625). In the same line of thinking, a 0 can be added to a number with an odd number of digits in order be even for example, 525 would be changed to 0525. While this seems unnecessary because the number is still really the same value, computers can interpret them differently so it is important to be consistent with following these rules. | A second method of doing pseudo RNG is with a middle square generator. This method takes an input value or seed, and squares it. The resulting number then has its middle digits extracted to be the same length as the original seed, and then this number is used as the next seed. For example, if our initial seed was 3592, we would square it to get 12,902,464. Because our initial seed was 4 digits long, we would drop the 12 at the start and 64 at the end of the number to get our next seed, 9024. This method of RNG does require our squared seed to have twice the number of digits of the initial number, and requires the seed to have an even number of digits. Obviously, there are many numbers that do not follow these rules, so in order to compensate we can add a 0 to the start of a number. In the case of a squared seed not having twice the digits (such as 25*25 = 625), a 0 is added to the squared number to obey the rule (0625). In the same line of thinking, a 0 can be added to a number with an odd number of digits in order be even for example, 525 would be changed to 0525. While this seems unnecessary because the number is still really the same value, computers can interpret them differently so it is important to be consistent with following these rules. | ||
=== Comparison between True and Pseudo random generation, conclusion=== | === Comparison between True and Pseudo random generation, conclusion=== | ||
| − | + | [[File:Pixabay.png|1024px|thumbnail|picture from Pixabay]] | |
PRNG have higher convenience, since all you need is a computer and an algorithm, but a TRNG requires an external device that is costly and may need to maintain the working condition consecutively to avoid damage. However, for the cyber security part, the TRNG takes the cake. For a sequence of true random numbers, there is no relation between subsequent values besides the fact that they come from the same source of entropy, which make TRNG numbers nearly impossible to predict, and therefore much safer defenses against cyber attacks. Another disadvantage for PRNGs is that they are deterministic; because each number in the sequence relies on previous ones, they are much easier to decrypt. | PRNG have higher convenience, since all you need is a computer and an algorithm, but a TRNG requires an external device that is costly and may need to maintain the working condition consecutively to avoid damage. However, for the cyber security part, the TRNG takes the cake. For a sequence of true random numbers, there is no relation between subsequent values besides the fact that they come from the same source of entropy, which make TRNG numbers nearly impossible to predict, and therefore much safer defenses against cyber attacks. Another disadvantage for PRNGs is that they are deterministic; because each number in the sequence relies on previous ones, they are much easier to decrypt. | ||
Revision as of 12:22, 29 November 2022
Contents
Random Number Generation In Modern Computer
Introduction
Randomness is not something that truly exists very often in the natural world. Things tend to obey laws that make interactions predictable. However, sometimes it is important to be able to create a random number. In fact, humans have been interested in generating randomness for thousands of years. Ancient dice have been dug up and discovered that belonged to civilizations long ago. Things like dice or coins have been used by people to make decisions randomly as long as we have been around it seems. Random numbers are only something we have recently begun to understand and even more recently really began to need. Random numbers are constantly being used now in everyday life. Take online gambling as an example, blackjack is dependent on what numbers the dealer draws for the player. If the numbers are predictable, the game doesn't work and the player could figure out if they are going to win or lose. For this reason, it is important to create randomness in the game. Random numbers are also used all the time in modern video games, offering a way to generate new and unique worlds for a player. Random numbers also have uses outside of just entertainment. For example, they are vitally important in the world of cybersecurity and keeping electronic information safe. Math and numbers are typically thought of as anything but random, and follow strict rules around changing them. For this reason creating randomness is a unique challenge seen in modern mathematics that has been approached with several different unique strategies.
Method
Almost all random number generation involves the use of some sort of seed in order to create the number. A seed is a number that is taken from somewhere and put into an algorithm to generate the random number. Then, the newly generated number is used as the seed for the next generation. Getting the initial seed is what makes this random. This can be done by using the current time, atmospheric noise, or some other source that can provide an unpredictable value. To give an example of how this might work, we will use time to generate a seed. If you were to call on a random number generator at 11:38, the random number generator could use the current time to the millionth decimal place as a seed in order to create an unpredictable value that could not be replicated.
There are two main types of RNG: pseudo RNG, and true RNG. Pseudo RNG means that the numbers generated follow some sort of pattern, and could theoretically be predicted. In most scenarios, this isn’t a big deal. For example in a video game like Mario Kart, if the item a player is going to get from a mystery box is technically predictable or follows a pattern, it doesn’t matter too much as long as the player doesn’t catch on and is having fun. In something like online gambling however, any sort of predictability is very dangerous. If a person could predict when to bet big and make millions of dollars, that would obviously create problems. For this reason, sometimes true RNG is needed. True RNG is more complicated and difficult to do as it requires more instruments, but is more effective than pseudo RNG at creating unpredictable numbers.
True Random Generation In Computer
A truly random generator could provide a random number that is barely impossible to predict. we will not explore the true random generation in detail, because it actually is not highly relative with math. Generally, a traditional computer that has the basic component cannot generate a True random number, it has to be obtained by a specific device. These devices will convert some phenomenon into a number. Some examples of TRNG sources include atmospheric noise, time, and radioactive decay.
atmospheric noise uses processes occurring in the atmosphere for its RNG. Most often, it’ll capture the static generated by lighting flashes, which occur roughly 40 times per second. (Random.org is known to use atmospheric noise to generate random outcomes for all kinds of different scenarios). For times, the device will take the exact nano second when you click the mouse as a random number, just pick one from the sequence. There is also one kind of device that uses a method called Harvest Entropy to obtain a random number using radioactivity, because the nuclear decay is not predictable.
Psedo random number generation
The PRNG relies on algorithms and programs to generate a number sequence that seems to be random. but since it is using a fixed way to produce those numbers, it could actually be reproduced and predicted. This is because computer hardware is purely logical, which means it cannot provide an output without input and processing, however that is exactly what random numbers obtain from, no source and reason. so, As suggested by the prefix “pseudo”, the sequence isn’t actually random, it just looks like it. The two main components of a PRNG are an initial value or seed, and a pre-set algorithm. it following the next several step:
- receive a seed as the input;
- Generating a number according to the preset algorithm;
- take the output as the input for the next computation;
- repeat the process until specific time or required length is achieved
Pseudo random generators are deterministic and periodic. deterministic means that the number generated is fixed whatsoever as long as the seed and the algorithm is set, periodic means after a certain amount of recursion, the algorithm will start to provide a repeated number. A good generator should last a long period.
Here is two examples of popular random generation algorithm that is currently used:
Linear Congruential Algorithm
One algorithms of an algorithm used for pseudo-RNG is the linear congruential algorithm shown below.
In this algorithm, Xn is the seed, so X₀ would be our initial seed gathered from one of the random methods we discussed. “a” is the multiplier in this formula, c is the increment, and m is the modulus. Both a and c must be greater than 0 and less than m. This way, with a pseudo random seed number, we can use this algorithm to continue to generate numbers that would be functionally random, as long as the multiplier, increment, and modulus are unknown.
For example, we let X₀ = 235, a = 2,398, c = 8,738, and m=1,000,000 since we had the seed already, we an go into the next step, make the formula and finish the calculation.
1,000,000 fits into 572,268 0 times, leaving a remainder of 572,268
Our X₁ is 572,268, so to get our X₂, we just have to use our formula again
1,000,000 fits into 1,372,307,402 1372 times, leaving a remainder of 307,402.
by repeating these steps, we got the first 5 array of random number as follows: 572268, 307402, 158734, 652870, and 590998. they looks pretty random, and that's how the algorithms work
Middle-Square algorithm
A second method of doing pseudo RNG is with a middle square generator. This method takes an input value or seed, and squares it. The resulting number then has its middle digits extracted to be the same length as the original seed, and then this number is used as the next seed. For example, if our initial seed was 3592, we would square it to get 12,902,464. Because our initial seed was 4 digits long, we would drop the 12 at the start and 64 at the end of the number to get our next seed, 9024. This method of RNG does require our squared seed to have twice the number of digits of the initial number, and requires the seed to have an even number of digits. Obviously, there are many numbers that do not follow these rules, so in order to compensate we can add a 0 to the start of a number. In the case of a squared seed not having twice the digits (such as 25*25 = 625), a 0 is added to the squared number to obey the rule (0625). In the same line of thinking, a 0 can be added to a number with an odd number of digits in order be even for example, 525 would be changed to 0525. While this seems unnecessary because the number is still really the same value, computers can interpret them differently so it is important to be consistent with following these rules.
Comparison between True and Pseudo random generation, conclusion
PRNG have higher convenience, since all you need is a computer and an algorithm, but a TRNG requires an external device that is costly and may need to maintain the working condition consecutively to avoid damage. However, for the cyber security part, the TRNG takes the cake. For a sequence of true random numbers, there is no relation between subsequent values besides the fact that they come from the same source of entropy, which make TRNG numbers nearly impossible to predict, and therefore much safer defenses against cyber attacks. Another disadvantage for PRNGs is that they are deterministic; because each number in the sequence relies on previous ones, they are much easier to decrypt.