| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[Category:ECE302Fall2008_ProfSanghavi]] | ||
| + | [[Category:probabilities]] | ||
| + | [[Category:ECE302]] | ||
| + | [[Category:problem solving]] | ||
| + | =Question= | ||
There is a stick of length 1. We break it at a random spot and take the leftmost part as a stick of length x. Then we break THAT stick at a random spot and take the leftmost part as a stick of length y. Find the PDF of Y. | There is a stick of length 1. We break it at a random spot and take the leftmost part as a stick of length x. Then we break THAT stick at a random spot and take the leftmost part as a stick of length y. Find the PDF of Y. | ||
| + | =Answer= | ||
f(x) = 1 for 0 < x < 1<br> | f(x) = 1 for 0 < x < 1<br> | ||
f(x) = 0 otherwise | f(x) = 0 otherwise | ||
| Line 24: | Line 30: | ||
<math>= \int_{y}^{1}\frac{1}{x} dx</math><br> | <math>= \int_{y}^{1}\frac{1}{x} dx</math><br> | ||
<math>= ln(\frac{1}{y}), 0 < y < 1</math><br> | <math>= ln(\frac{1}{y}), 0 < y < 1</math><br> | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Main_Page_ECE302Fall2008sanghavi|Back to ECE302 Fall 2008 Prof. Sanghavi]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:23, 22 November 2011
Question
There is a stick of length 1. We break it at a random spot and take the leftmost part as a stick of length x. Then we break THAT stick at a random spot and take the leftmost part as a stick of length y. Find the PDF of Y.
Answer
f(x) = 1 for 0 < x < 1
f(x) = 0 otherwise
We also know that
fY|X(y|x) = 1/x for 0 < y < x
fY|X(y|x) = 0 otherwise
This is the graph of fY|X(y|x):
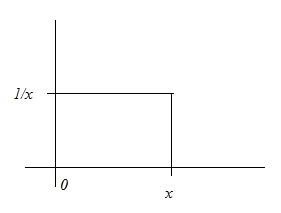
Using the theorem of total probability for continuous RVs, we have that
$ f_{Y}(y) = \int_{-\infty}^{\infty}f_{Y|X}(y|x)f_{X}(x) dx $
$ = \int_{0}^{1}f_{Y|X}(y|x)(1) dx $
because we are doing an integral of x, and the probability that x < y or x > 1 is 0, the limits of integration become from y to 1:
$ = \int_{y}^{1}\frac{1}{x} dx $
$ = ln(\frac{1}{y}), 0 < y < 1 $